The Philistines were an ancient people who inhabited the southern coast of Canaan during the Iron Age (Philistia). They are often depicted in the Bible as being the archenemies of the Israelites, with their conflicts with the Israelites forming a significant part of the narrative of the Old Testament.

Credit: Olaf Tausch, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
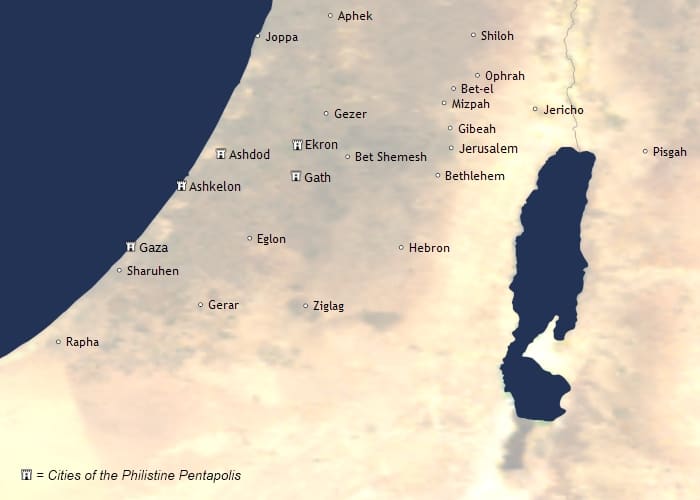
The Philistines were originally from the Aegean region and migrated to Canaan around the 12th century BCE. They established five city-states along the southern coast of Israel (Philistia), including Gaza, Ashdod, Ashkelon, Gath, and Ekron. These cities were strategically located along important trade routes, which made them important economic centers.
The Philistines are first mentioned in historical sources in the late 12th century BCE, shortly after the period of Sea People activity in the region. They are believed to have migrated to the eastern Mediterranean from the Aegean region, although the exact circumstances of their arrival and settlement are still a subject of debate among scholars.
The Sea People
Some scholars have suggested that the Philistines may have been a group of Sea People who settled in the coastal region of Palestine. In contrast, others argue that the Philistines were a distinct group that arrived in the region several centuries after the Sea People. Evidence suggests that the Philistines were a powerful and influential group in the eastern Mediterranean during the Iron Age, with their territory covering much of the coastal plain of what is now modern-day Israel and the Gaza Strip.
Credit: Cush, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Philistines were known for their advanced military technology, including iron weapons and chariots. They were also skilled sailors and traders, allowing them to expand their influence throughout the Mediterranean. The Philistines were frequently at war with the Israelites, who were their neighbors to the east. The conflict between the two peoples is depicted in the Bible as a struggle for control over the land of Canaan.
Museum for Philistine Culture
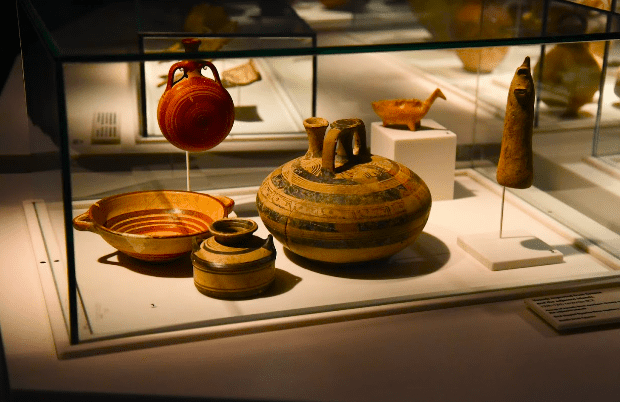

So the most famous battle between the Israelites and their archenemies was between David and Goliath, often used to symbolize the underdog’s triumph. Despite their reputation as enemies of the Israelites, the Philistines were also involved in cultural exchange with their neighbors. They adopted some aspects of Israelite culture, such as the worship of Yahweh, while also maintaining their own unique identity.
Ultimately, the Babylonians defeated them in the 6th century BCE, destroying their cities. However, their legacy lives on in the cultural memory of the region. Today, “Philistine” refers to someone uncultured or uncivilized, but this is a far cry from the sophisticated civilization that the Philistines represented.







