The Lower Paleolithic era holds a significant place in studying human evolution. During this period, various cultures emerged, leaving traces of their existence and shedding light on our early ancestors’ lives. Among these industries, the Acheulean Industry stands out as a notable example. This post will delve into the Acheulean culture’s presence in the Land of Israel, unearthing intriguing insights into our human heritage.
Credit: CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
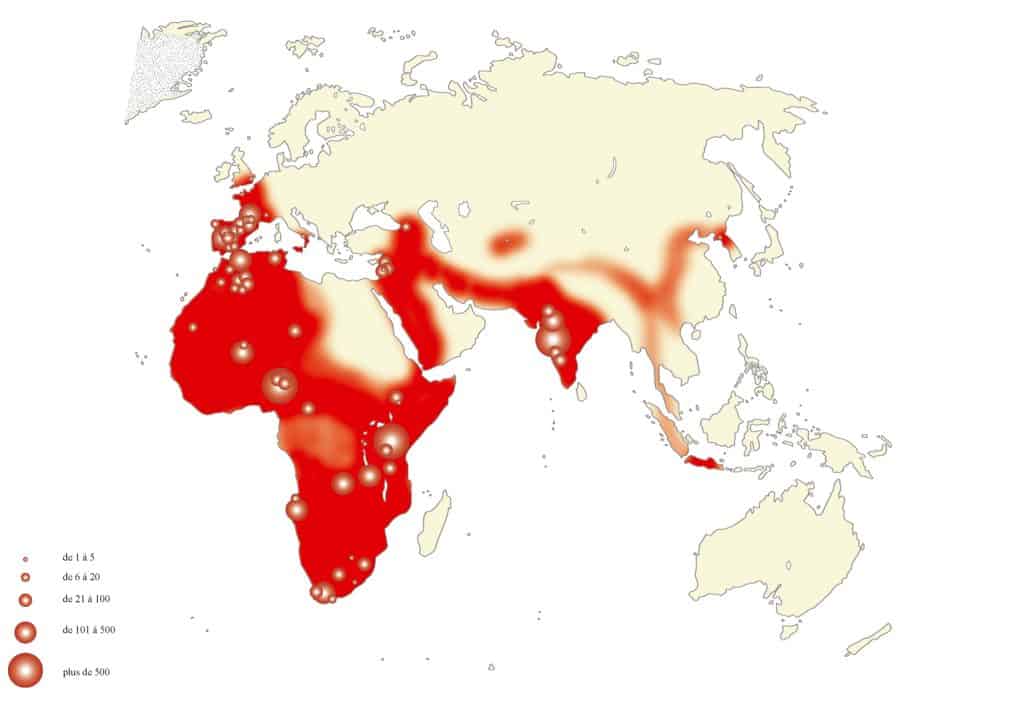
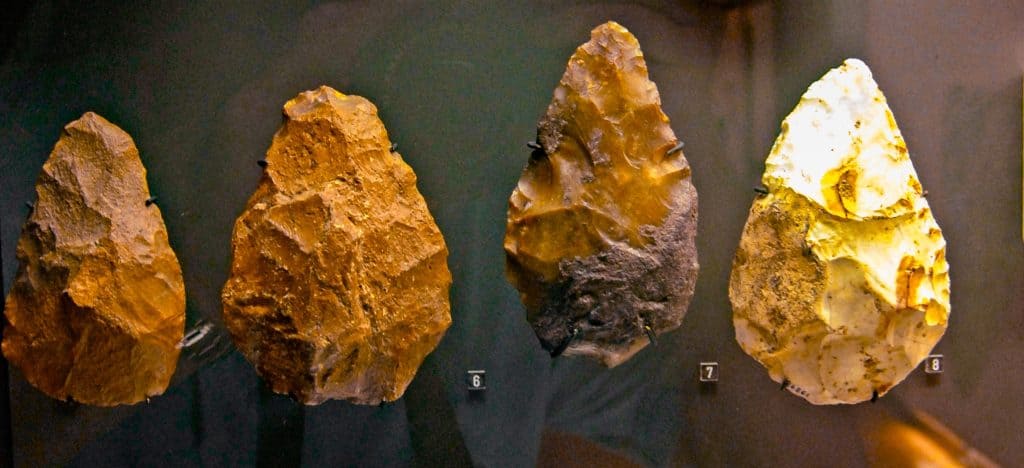
The Acheulean Industry is named after the site of Saint-Acheul in France, where early stone tools were first discovered in the mid-19th century. It flourished from approximately 2.6 million to 300,000 years ago during the Lower Paleolithic period. The Acheulean culture represents a substantial technological advancement in stone tools, characterized by the creation of standardized bifacial hand axes and cleavers. Furthermore, Acheulean toolmakers primarily used hard hammer percussion to shape their tools. This technique involved striking a stone core with a hammerstone to remove flakes and shape the tool. The flakes were further refined by pressure flaking, which involved applying controlled pressure to the edges to create a sharp cutting surface.
The Land of Israel and Acheulean Industry:
The Land of Israel is a region with rich historical and archaeological significance. Humans have inhabited it for thousands of years, and evidence of the Acheulean culture has been found at various sites within its borders. These discoveries shed light on the early human presence in this region and their way of life.
Stone Age Tour
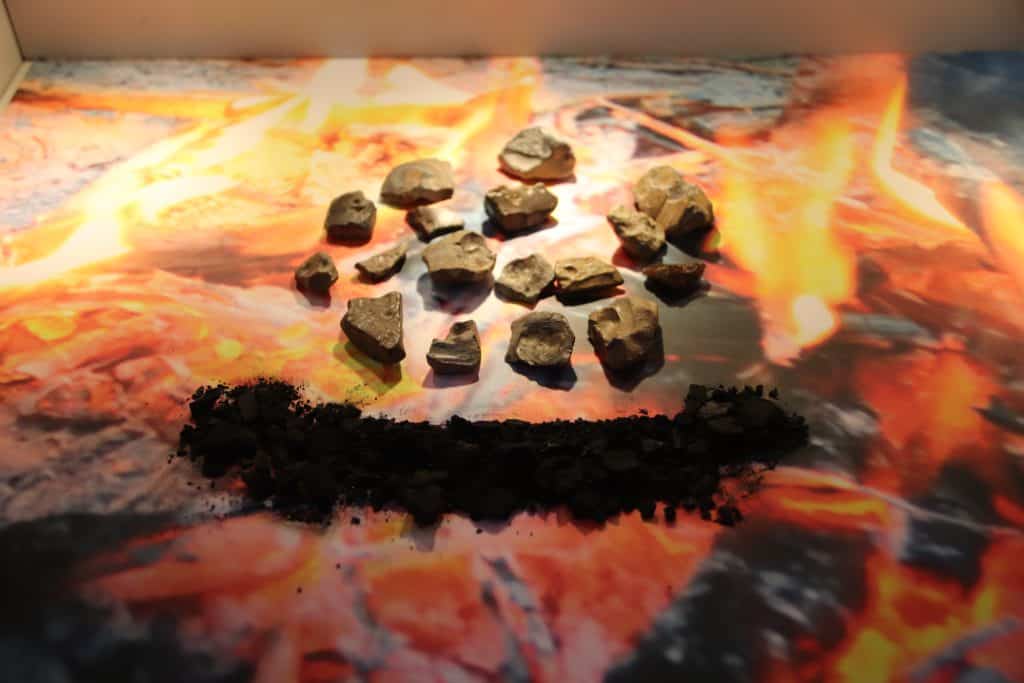

One notable site is Gesher Benot Ya’aqov, located in the Hula Valley in northern Israel. This site has provided archaeologists with valuable insights into the Acheulean culture. Excavations at Gesher Benot Ya’aqov have revealed a complex settlement, showcasing evidence of long-term human occupation and sophisticated tool-making techniques. The inhabitants of this site utilized local resources, such as flint and basalt, to craft their stone tools.
Another significant Acheulean site in the Land of Israel is Qesem Cave near Tel Aviv. Excavations at Qesem Cave have uncovered many Acheulean artifacts, including hand axes, scrapers, and flint flakes. The site’s exceptional preservation conditions have allowed researchers to explore the tools and the food remains, fire hearths, and evidence of early human consumption patterns.
Implications and Significance:
The presence of the Acheulean Industry in the Land of Israel has profound implications for our understanding of human evolution and migration patterns. The region’s strategic location at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and Europe suggests that it played a crucial role in dispersing early humans.

Credit: Jochen Jahnke, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
So the Acheulean Industry’s technological advancements, particularly in tool-making, indicate cognitive abilities and problem-solving skills. Moreover, these developments mark significant milestones in our ancestors’ journey, paving the way for future cultural and technological progress.
Furthermore, the Acheulean sites in the Land of Israel contribute to a broader global narrative, linking the human story across continents and emphasizing our early ancestors’ shared origins and achievements.
Conclusion:
So the Acheulean Industry in the Lower Paleolithic era has left an indelible mark on human history. Furthermore, its presence in the Land of Israel, as evidenced by the archaeological finds at Gesher Benot Ya’aqov and Qesem Cave, highlights the significance of this region in the human narrative. The Acheulean Industry’s sophisticated tool-making techniques and exploring local resources provide valuable insights into our early ancestors’ ingenuity and adaptability.
Last, studying the Acheulean Industry in the Land of Israel enhances our understanding of human evolution, migration patterns, and cultural diversity during the Lower Paleolithic era. Ultimately these discoveries stand as a testament to our ancient predecessors’ resilience and remarkable capabilities, laying the foundation for the awe-inspiring story of human development that continues to unfold.







