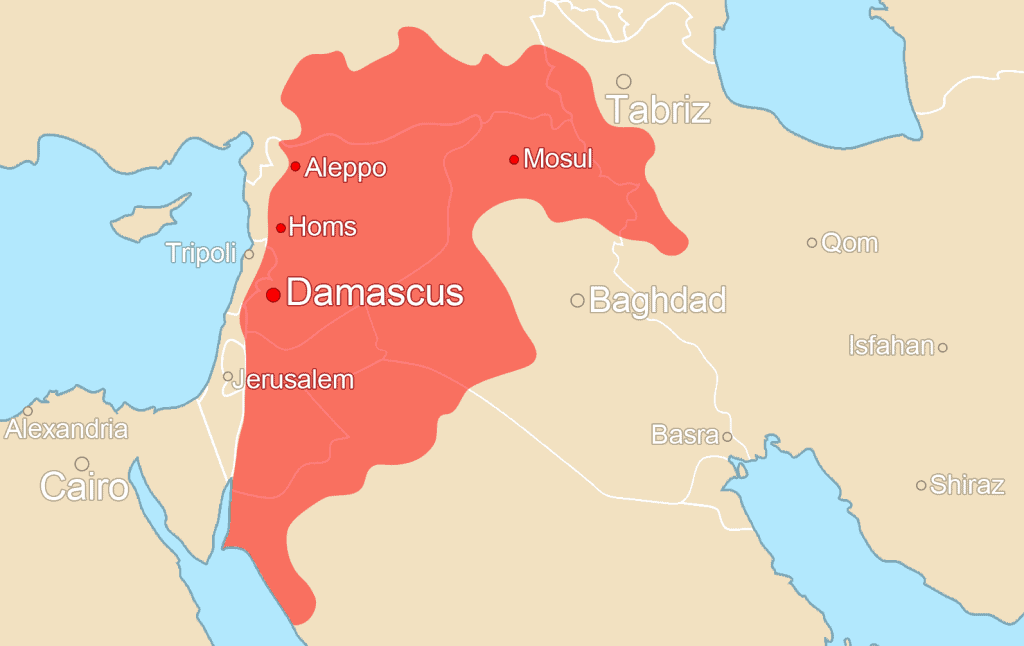
The Zengid dynasty originated from the Turkish Zengid tribe of Oghuz Turkic descent. Their rise to power can be traced to Imad ad-Din Zengi, who became the governor of Mosul in northern Mesopotamia in 1127. Imad ad-Din Zengi is considered the founder of the dynasty.
Imad ad-Din Zengi
Imad ad-Din Zengi is perhaps the most famous figure of the Zengid dynasty. He was known for his military prowess and political acumen. Imad ad-Din Zengi’s achievements included the capture of Aleppo in 1128 and his efforts to unite Muslim forces against the Crusaders during the Second Crusade. His death in 1146 marked a turning point in the dynasty’s history.
Nur Ad-Din

Nur ad-Din
Imad ad-Din Zengi was succeeded by his son, Nur ad-Din, who ruled over Aleppo and northern Mesopotamia. Nur ad-Din continued his father’s efforts to resist the Crusaders and sought to expand his influence in the region. He formed a crucial alliance with Salah ad-Din (Saladin) and played a significant role in the recapture of Jerusalem in 1187.
Zengi

Decline and Fragmentation
After the death of Nur ad-Din in 1174, the Zengid dynasty faced internal strife and external pressures from other regional powers. The dynasty began to fragment, with various branches of the Zengid family ruling different territories.
Legacy
The Zengid dynasty’s legacy lies in its resistance against Crusader expansion and its contributions to the broader history of the Middle East during the medieval period. Imad ad-Din Zengi and Nur ad-Din, in particular, are remembered for their efforts to unite Muslim forces against the Crusaders and promote Sunni Islam in the territories they ruled.
Influence on the Crusades
The Zengids played a significant role in shaping the Crusades. Their military campaigns and political maneuvering influenced the strategies and alliances of both Crusader and Muslim forces during this tumultuous period of history.
End of the Dynasty
The Zengid dynasty gradually declined and lost significance in the late 12th century. It was ultimately absorbed into the Ayyubid dynasty, founded by Salah ad-Din (Saladin).
In summary, the Zengid dynasty, founded by Imad ad-Din Zengi and continued by his son Nur ad-Din, was a notable player in the medieval Middle East. Their efforts to resist Crusader advances and promote Sunni Islam left a lasting mark on the region’s history, and their legacy is intertwined with the broader narrative of the Crusades and the complex political landscape of the Levant during that era. More about the subject in Wikipedia!







