Welcome to a captivating journey through time as we delve into the remarkable world of the Natufian culture, a pivotal chapter in the story of human civilization during the Neolithic period. Join me as we uncover this ancient society’s key aspects and lasting influence.
Credit: Crates, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
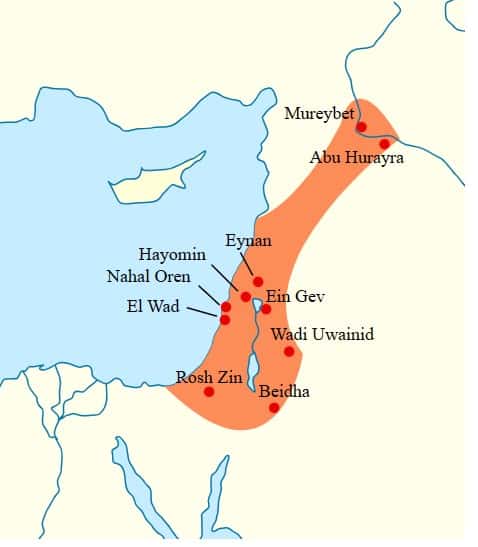
First, the Natufian culture flourished in the Levant region, encompassing present-day Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan, approximately 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. Furthermore, the culture spans the transition from hunter-gatherers to early agricultural societies. Moreover, the Natufians played a significant role in developing settled communities and developing agriculture.
Natufuan Culture Settlement Patterns
Unlike previous hunter-gatherer societies, the Natufians began to establish semi-permanent settlements, marking a notable shift in human lifestyle. These settlements were often situated in favorable locations near water sources, such as the Jordan Valley and the Mediterranean coast, enabling reliable access to vital resources for survival.

Credit: R Yeshurun, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Architectural Ingenuity
Natufian settlements showcased impressive architectural advancements. They constructed semi-subterranean dwellings made of stone and mud, which offered protection from the elements and insulation from temperature fluctuations. Some structures featured multiple rooms, indicative of communal living and the development of social structures within the society.
Early Agricultural Practices
Although predominantly hunter-gatherers, the Natufians gradually began to cultivate and harvest wild cereals. This marked an essential step toward agricultural practices, paving the way for the domestication of plants in subsequent Neolithic cultures. The Natufians employed techniques such as reaping, grinding, and storing grain, demonstrating their increasing reliance on cultivated resources.
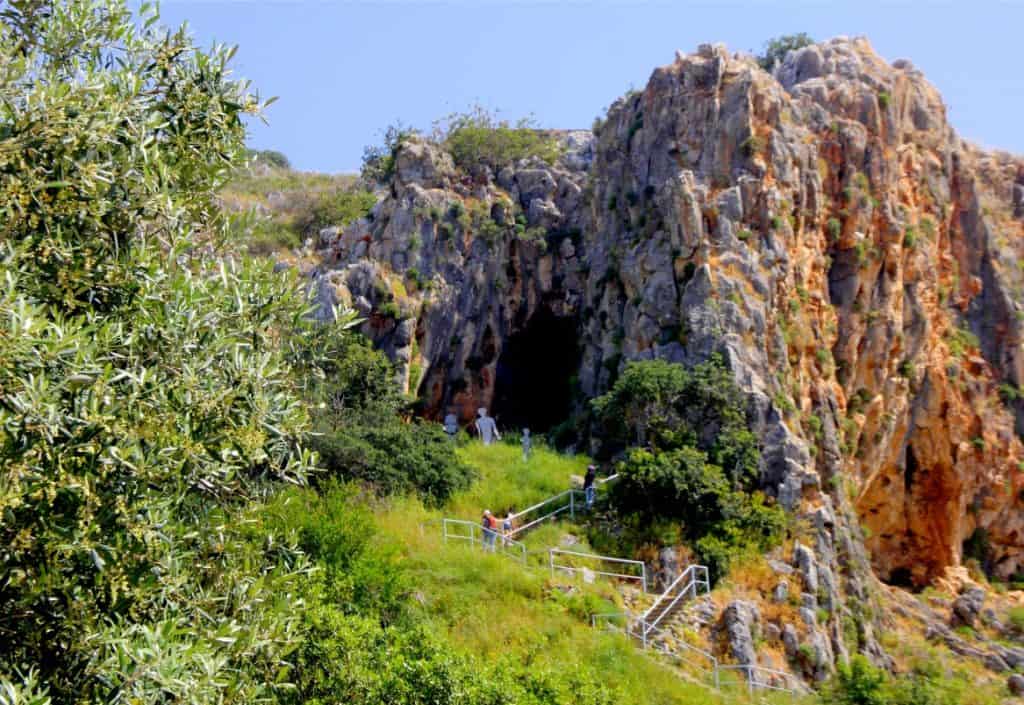
Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve

Technological Advancements
The Natufians exhibited remarkable progress in tool-making, utilizing stone tools for various purposes. Microliths—small, sharp stone flakes—became a defining feature of their toolkit. These microliths were skillfully crafted and employed for hunting, woodworking, and sewing, showcasing the Natufians’ expertise in crafting specialized implements.
Natufian Culture Artistic Expressions
Artistic expression was an integral part of the Natufian culture. Furthermore, the people created intricate and delicate objects from various materials, including bone, ivory, and stone. Examples include engraved or sculpted figurines, jewelry, and decorative items. So these artifacts provide insights into their spiritual beliefs, social customs, and aesthetic sensibilities.
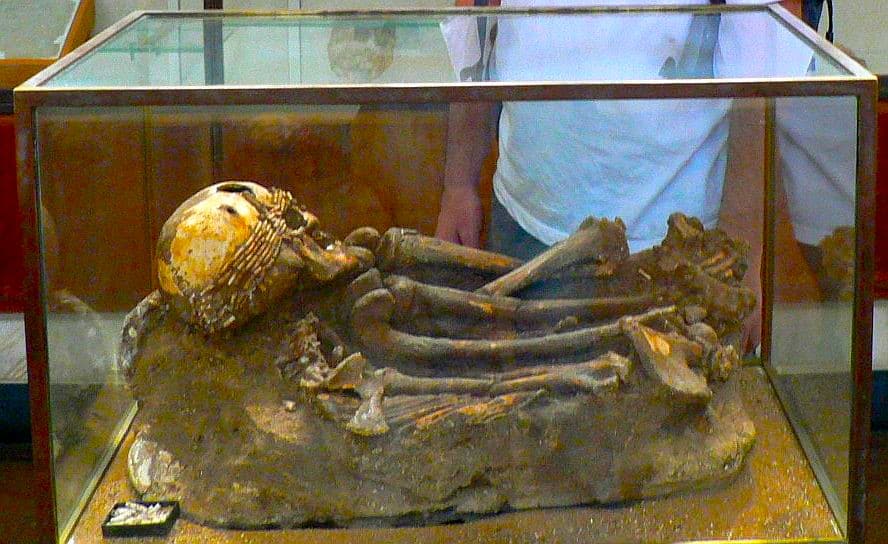
Burial Customs and Rituals
In addition, the Natufians practiced burial rituals, often interring their deceased within their settlements. Grave goods, such as ornate jewelry and tools, were frequently placed alongside the deceased, suggesting a belief in an afterlife or a spiritual connection with the buried items. These burial customs provide glimpses into their complex belief systems and cultural practices.
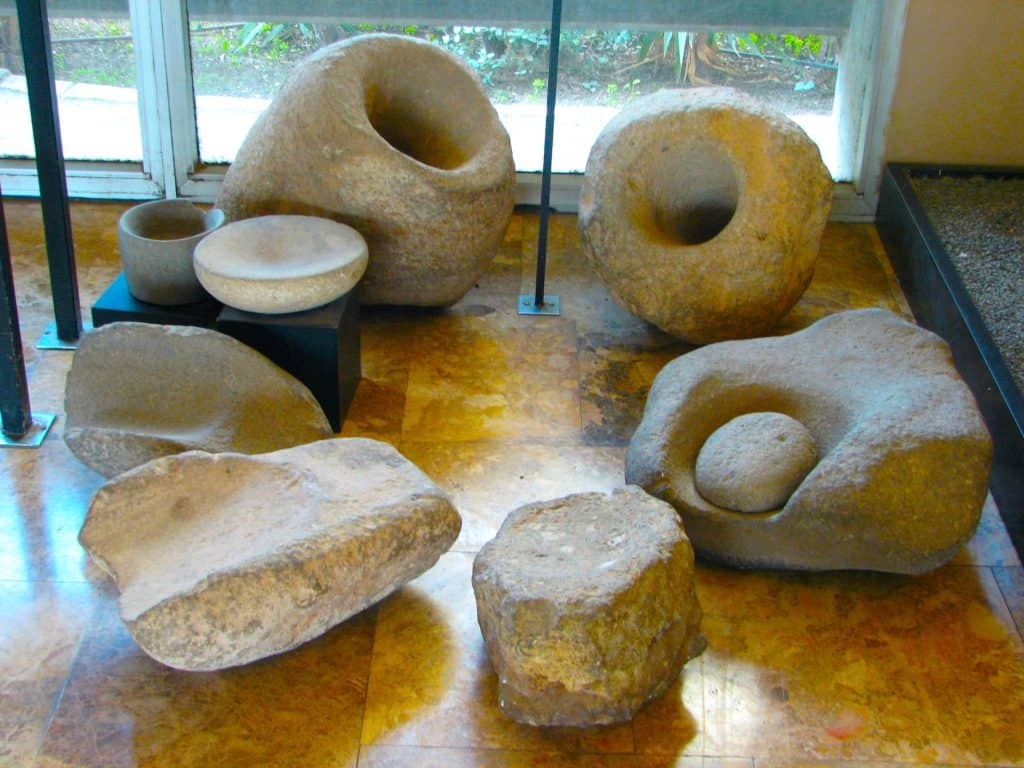

Credit: Hanay, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Legacy and Influences:
Furthermore, the Natufian culture laid the foundation for the subsequent agricultural societies that emerged during the Neolithic period. Moreover, their experimentation with plant cultivation, developing settled communities, and technological advancements set the stage for transitioning from nomadic lifestyles to more sedentary agricultural civilizations.
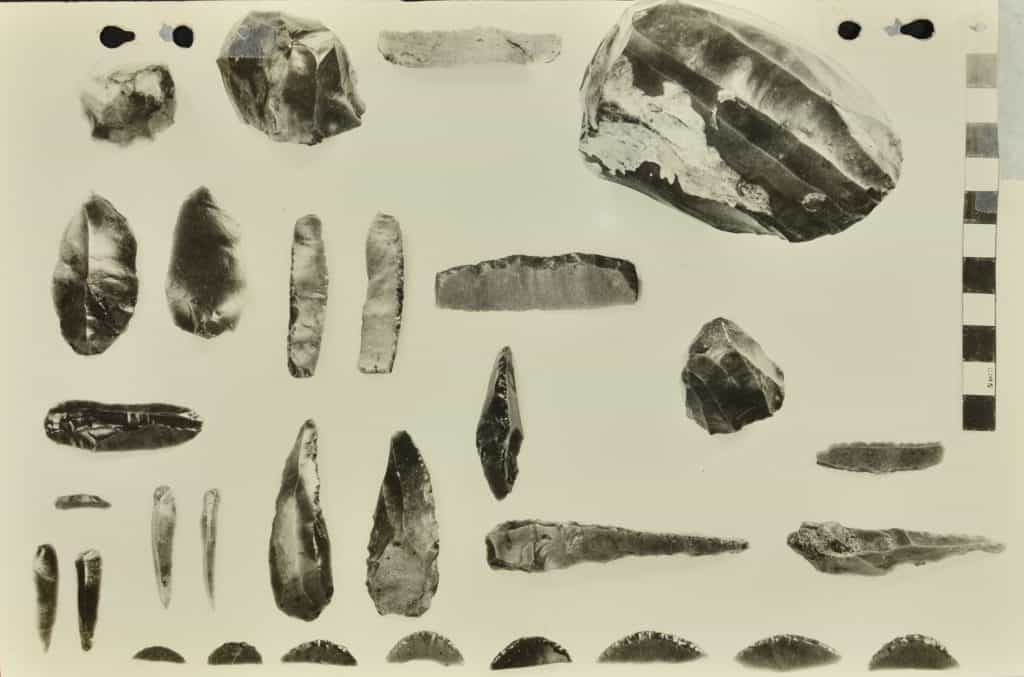

Credit: Israel Antiquities Authority, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Continuing Research and Discoveries
Last, ongoing archaeological excavations and research continue to expand our knowledge of the Natufian culture and its significance. New findings contribute to our understanding of their social structures, subsistence strategies, and interactions with neighboring communities, painting a more comprehensive picture of their daily lives and contributions to human history.







