During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the Jewish land purchase efforts in Palestine were integral to the Zionist movement’s goal to establish a Jewish homeland in the region. These efforts involved the acquisition of land for Jewish settlement and development to create the infrastructure necessary for establishing a future Jewish state. Here’s an overview of Jewish land purchases in Palestine:
The Sursock Purchase
Zionist Movement and Land Acquisition:
The Zionist movement, founded by Theodor Herzl in the late 19th century, sought to create a national homeland for the Jewish people in Palestine, which was then part of the Ottoman Empire. Central to this goal was acquiring land for establishing Jewish communities.
Yehoshua Hankin

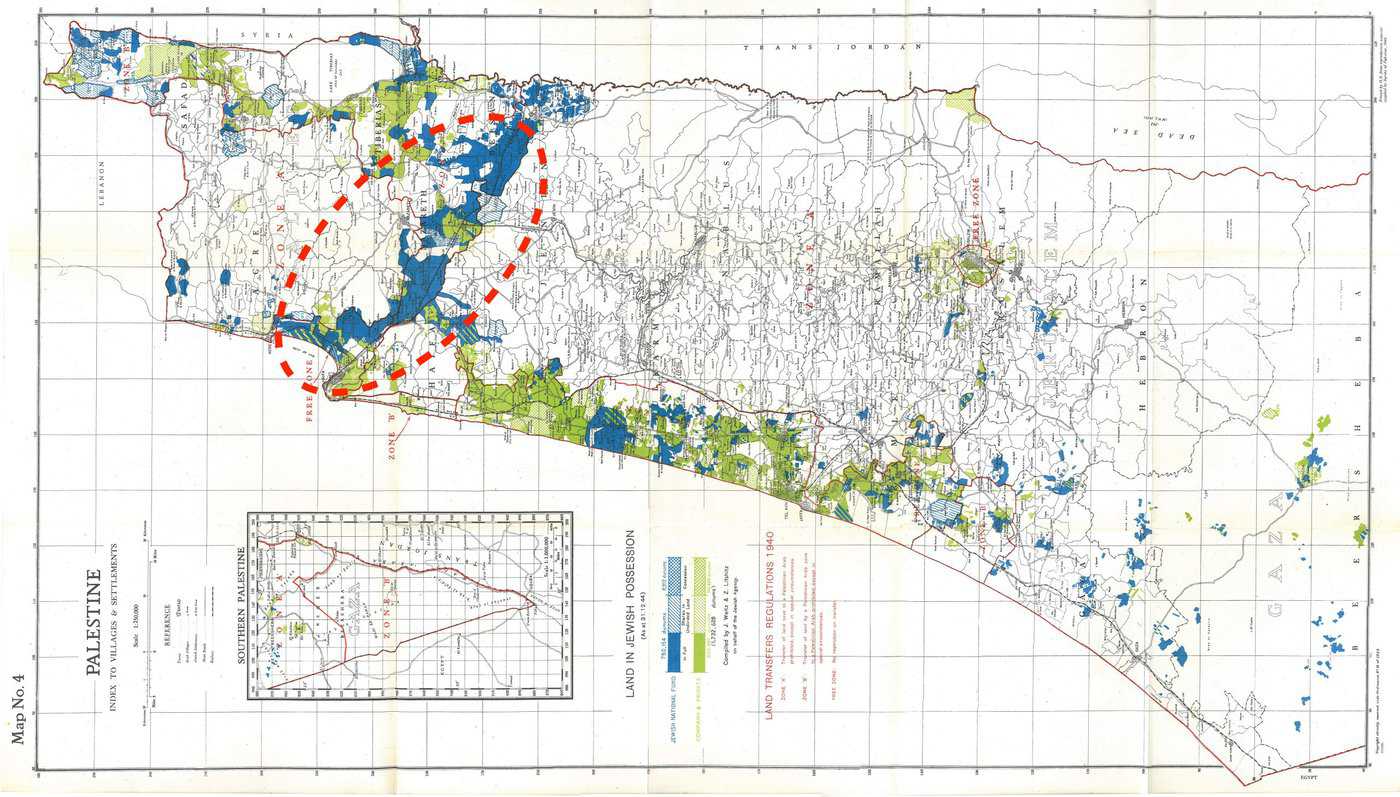
Jewish National Fund (JNF): The Jewish National Fund was a key institution facilitating land acquisition. Established in 1901, the JNF aimed to buy and develop land in Palestine for Jewish settlement. It relied on donations from Jewish communities worldwide to purchase land and develop various projects, such as afforestation and infrastructure.

Credit: MathKnight and Zachi Evenor, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Land Purchase and Development:
Jewish land purchase efforts were driven by various factors, including the desire to establish agricultural communities, create employment opportunities, and provide a haven for Jewish populations facing persecution in other parts of the world. The land was often purchased from Arab landowners through negotiations or agreements facilitated by intermediaries.
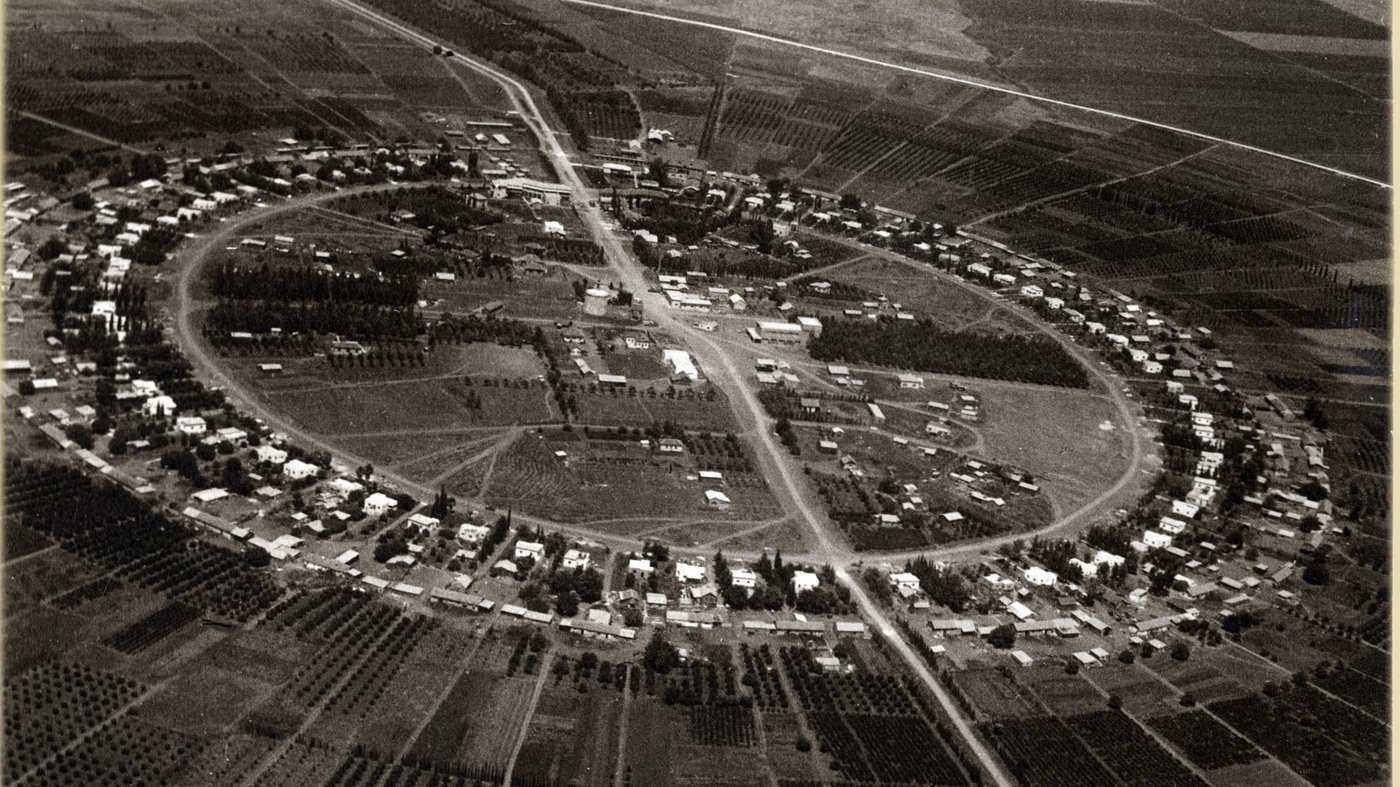

Kibbutzim and Agricultural Settlements: Many land purchases were used to establish kibbutzim (collective agricultural communities) and moshavim (cooperative farming villages). These settlements were designed to promote agricultural development, self-sufficiency, and a strong sense of community among Jewish immigrants. Below in the Video, you can see the Mausoleum of Yehoshua Hankin, which he’s buried in the Jezreel Valley.
Challenges and Conflicts: The influx of Jewish immigrants and the establishment of new settlements led to tensions with the Arab population already living in Palestine. As Jewish land purchases increased, concerns over the displacement of Arab residents and the impact on Arab livelihoods also grew. These tensions laid the groundwork for the Arab-Jewish conflict in the region.

British Mandate Period: After World War I, the League of Nations granted Britain the mandate to govern Palestine. During this period (1920-1948), Jewish land purchases continued, sometimes with British support and sometimes in the face of restrictions imposed by British authorities due to the mounting tensions between Jewish and Arab communities.
Impact on Israeli Statehood:
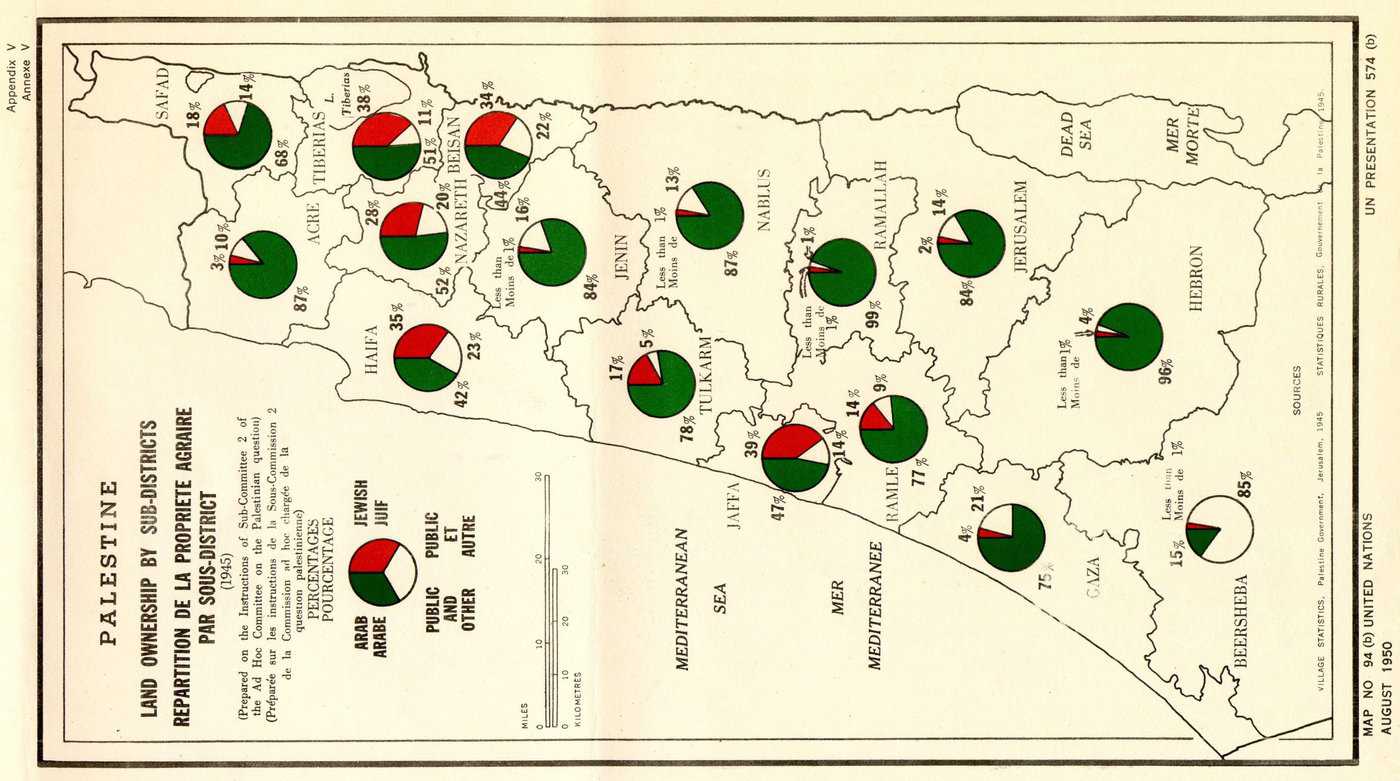
The land purchased and developed during these early decades laid the foundation for the modern State of Israel, established in 1948. Many areas settled by Jewish immigrants became integral parts of the new state.
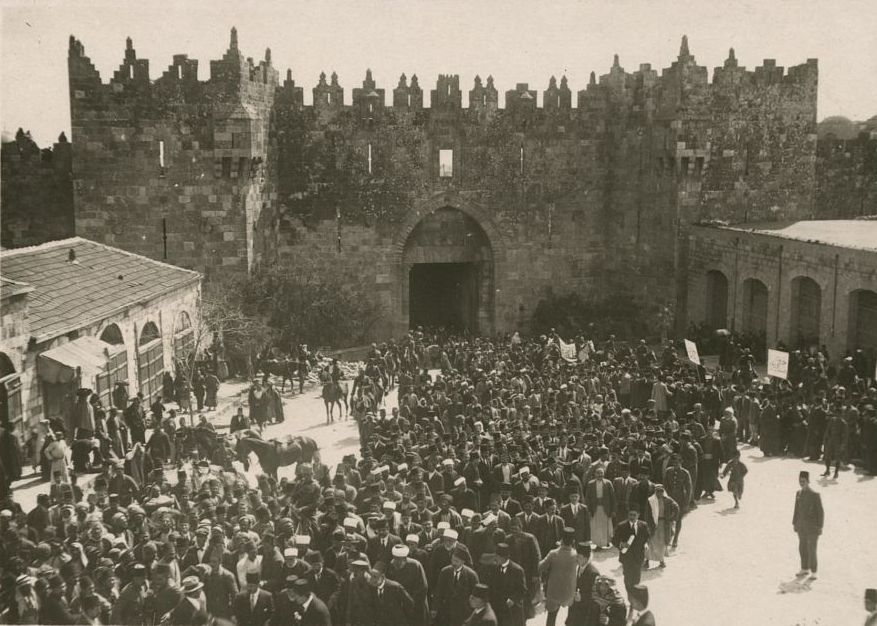

Legacy and Controversy: Jewish land purchase in Palestine remains complex and debated. While these efforts were driven by the goal of establishing a Jewish homeland, they were also intertwined with tensions between Jewish and Arab communities. The legacy of these land acquisitions continues to influence discussions surrounding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Jezreel Valley Day Tour

Jewish land purchases in Palestine played a significant role in the Zionist movement’s efforts to establish a Jewish homeland and contributed to the development of modern Israel. However, it also shaped the dynamics and challenges of the region, setting the stage for the current complex historical and political landscape.

