The Treaty of Jaffa, signed in 1192, marked a crucial moment in the aftermath of the Third Crusade, a conflict between European Christian forces and Saladin’s Muslim armies over control of the Holy Land. This treaty, negotiated primarily between Richard the Lionheart (Richard I of England) and Saladin (Salah ad-Din), brought a temporary respite to the region and allowed certain Christian access to Jerusalem.
The Third Crusade
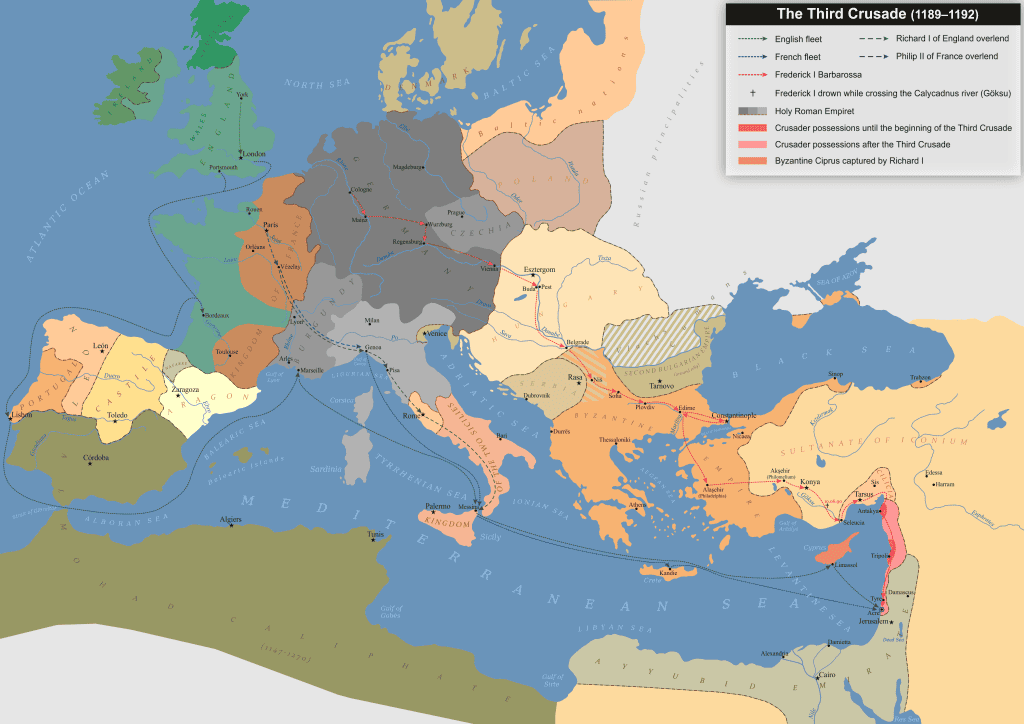
Background:
The Third Crusade had begun in response to the capture of Jerusalem by Saladin in 1187, a catastrophic event for Christendom. The loss of this holy city prompted Pope Gregory VIII to issue a call for a new Crusade, rallying European monarchs to take up the cause. Richard the Lionheart of England, Philip II of France, and Emperor Frederick I of the Holy Roman Empire were among the prominent leaders of this Crusade.
Saladin
Key Provisions of the Treaty of Jaffa:
Access to Jerusalem: One of the central provisions of the treaty was the guarantee of safe passage for Christian pilgrims to Jerusalem. While the city remained under Muslim control, the treaty allowed for peaceful and unarmed Christian visits for purposes of worship.
Territorial Gains: The treaty recognized the Christian Crusader states’ control over certain coastal cities, including Jaffa and Acre. These cities were crucial bases for continued Christian presence in the Holy Land.
Return of Christian Captives: Saladin agreed to release Christian captives who had been taken prisoner during the Third Crusade. This provision was a humanitarian gesture to improve relations between the two sides.
Ceasefire and Peace: The treaty established a truce, ending hostilities between Christian and Muslim forces in the region. It aimed to reduce the immediate threat of warfare and bloodshed.
Treaty of Jaffa and Its Significance:
Christian Presence in the Holy Land: The Treaty of Jaffa allowed for a limited but meaningful Christian presence in the Holy Land. While the ultimate goal of recapturing Jerusalem was not achieved, this provision provided a degree of access to the city’s religious sites for Christian pilgrims.
Diplomatic Achievement: The treaty demonstrated the diplomatic skill of both Richard the Lionheart and Saladin. It showcased their willingness to negotiate and reach compromises, even amid a bitter and protracted conflict.
Fragility of Peace: The peace established by the treaty was fragile and short-lived. It did not bring a definitive end to the Crusades, as conflicts and rivalries in the region persisted in the subsequent years.
In conclusion, the Treaty of Jaffa of 1192 is a testament to the complexities of diplomacy and the quest for religious access and control in the medieval Holy Land. While it did not fully satisfy the aspirations of either side, it temporarily eased tensions and allowed for some degree of peaceful coexistence in this historically charged region.







