The United Nations Partition Plan of Palestine, adopted on November 29, 1947, holds immense historical significance as a pivotal moment in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the establishment of the State of Israel. Let us delve into the details of this landmark decision and its enduring impact on the region.

Un Partition Plan for Palestine: Historical Context
So following World War I, the League of Nations mandated the British administration of Palestine. However, tensions between Jewish immigrants and the Arab population grew over conflicting national aspirations. As the British mandate neared its end, the question of Palestine’s future became an international concern.
The UN Partition Plan:
The United Nations proposed a partition plan for Palestine in response to mounting tensions. Moreover, the plan suggested dividing the territory into separate Jewish and Arab states and an internationally administered zone encompassing Jerusalem and Bethlehem—the proposal aimed to provide a solution to the competing national aspirations and establish peaceful coexistence.
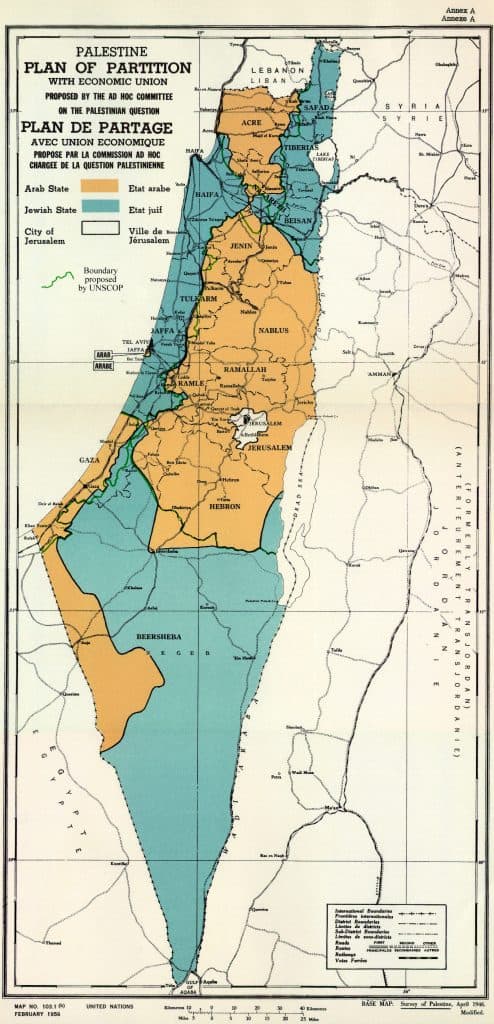
Un Partition Plan for Palestine: Key Provisions
The partition plan proposed dividing Palestine into roughly equal portions for the Jewish and Arab populations. It allocated about 56% of the land to the proposed Jewish state and about 43% to the Arab state, with the remaining 1% designated as an international zone. The plan also addressed issues such as citizenship, economic cooperation, and the protection of minority rights.
Reactions and Controversies:
The UN partition plan received mixed reactions from various parties. Jewish leaders accepted the plan as an opportunity to establish a homeland for the Jewish people. In contrast, Arab leaders and neighboring countries rejected it, arguing that it violated the rights of the Arab population and undermined the principle of self-determination.
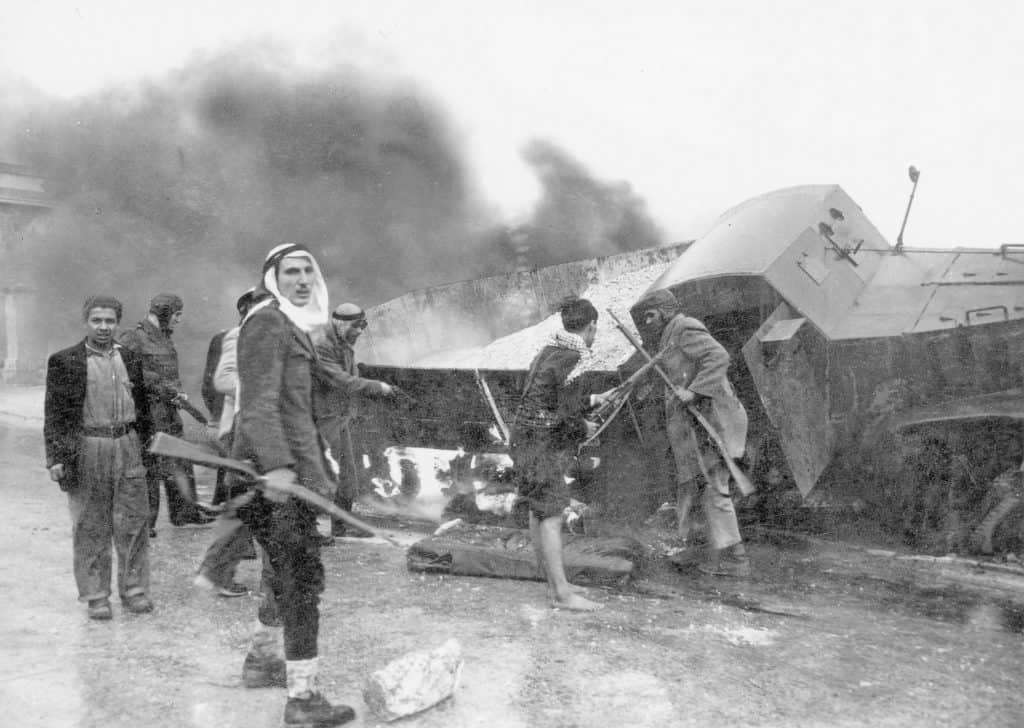
Immediate Aftermath
So adopting the partition plan marked a significant turning point in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The Jewish community accepted the plan and declared the establishment of the State of Israel on May 14, 1948. However, Arab countries rejected the new state and initiated military action, leading to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
UN General Assembly Resolution 181: Long-Term Impact
Furthermore, the UN partition plan laid the foundation for establishing Israel and contributed to the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict. While Israel accepted the plan and used it as a basis for its statehood, the Arab rejection and subsequent conflicts resulted in displacement, refugee crises, and territorial disputes that continue to shape the region’s dynamics today.
So the UN partition plan serves as a reminder of the complexities and challenges of resolving conflicts rooted in competing national aspirations. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict underscores the importance of dialogue, negotiation, and finding common ground to foster lasting peace and coexistence.
Pursuing Peace and Resolution:
Decades after the UN partition plan, efforts to achieve a comprehensive and lasting resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict persist. International organizations, mediators, and stakeholders continue to engage in peace negotiations, emphasizing the need for a two-state solution that addresses Israelis’ and Palestinians’ legitimate aspirations and concerns.
1947-1949 Arab Israeli War

A Hope for the Future:
Lastly, as we reflect on the UN partition plan of Palestine, let us embrace the vision of a peaceful coexistence where Israelis and Palestinians can live side by side in security, dignity, and mutual respect. May the lessons learned from history inspire us to work towards a future where everyone in the region can enjoy peace, prosperity, and harmonious coexistence.

