Welcome to the captivating world of the Middle Paleolithic period, a significant epoch in human history that witnessed the emergence and development of our ancient human ancestors. Join me as we embark on a remarkable journey through time to explore this transformative era’s cultural achievements, technological advancements, and intriguing aspects.
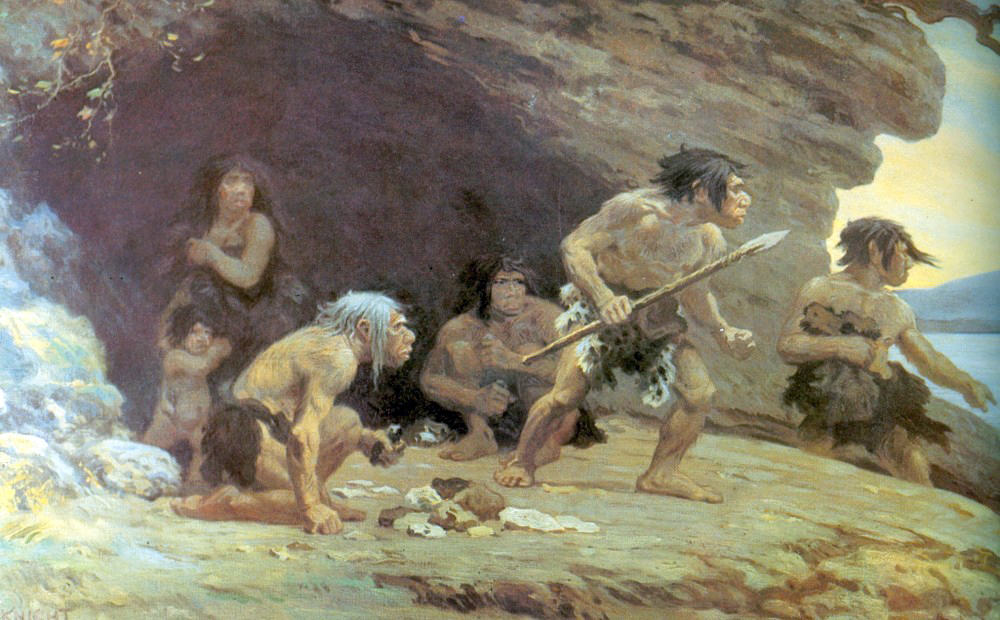

The Middle Paleolithic period, dated approximately 300,000 to 30,000 years ago, marked a crucial phase in human evolution. It falls within the larger framework of the Paleolithic era, characterized by the use of stone tools and the emergence of early human species.
Human Species:
Firstly, multiple human species coexisted during the Middle Paleolithic period, including Homo neanderthalensis (Neanderthals) and Homo sapiens (modern humans). Furthermore, these species exhibited remarkable adaptations to their environments, as evidenced by their tool-making abilities, social structures, and cultural expressions.
Middle Paleolithic Period: Technological Innovations
In addition, one of the defining features of the Middle Paleolithic period was the refinement and diversification of stone tool technologies. Moreover, our ancient ancestors developed more sophisticated toolkits, including handaxes, scrapers, and spear points, allowing them to hunt, butcher animals, and process materials more efficiently.
Controlled Use of Fire:
Evidence suggests that early humans during the Middle Paleolithic period began to harness and control fire. Fire served as a source of warmth, protection, and a tool for cooking food, extending the range of available food sources and aiding in colonizing diverse environments.
At Qesem Cave, evidence exists of the regular use of fire from 382,000 BP to around 200,000 BP. Furthermore, large quantities of burned bone and moderately heated soil lumps were found, and the cut marks on the bones suggest that butchering and prey-defleshing occurred near fireplaces. In addition, hominins living in Qesem cave managed to heat their flint to varying temperatures before knapping it into different tools.
Adaptation and Migration:
Middle Paleolithic communities exhibited impressive adaptability, allowing them to colonize various environments across Africa, Europe, Asia, and the Levant. Their ability to adapt to diverse climates and resource availability showcases their ingenuity and capacity to survive and thrive in different ecological niches.
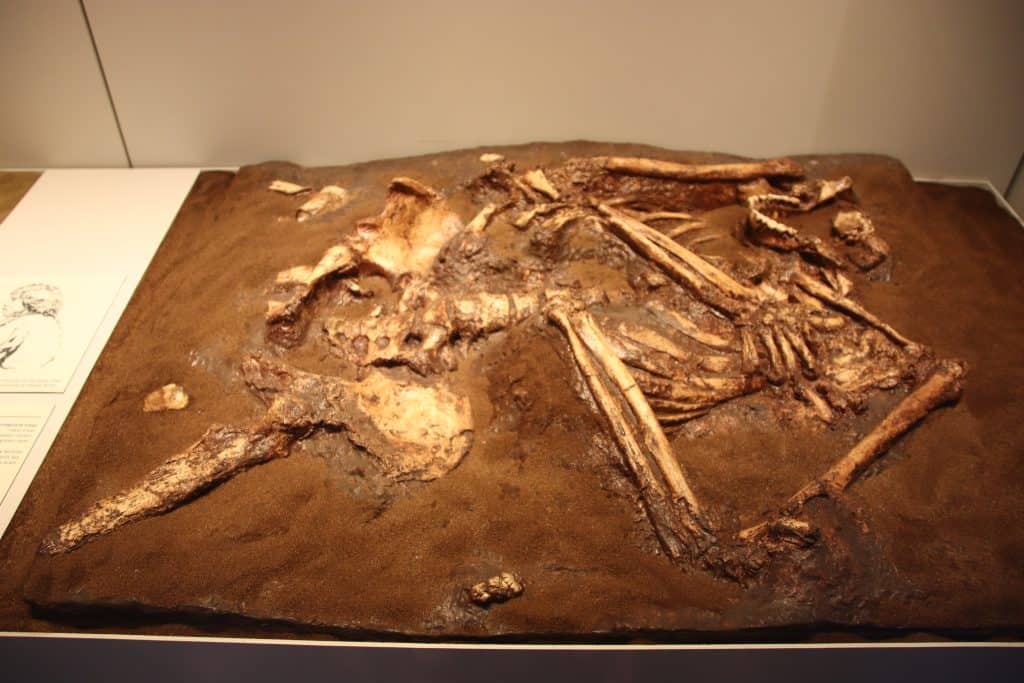

Subsistence Strategies:
Middle Paleolithic populations primarily relied on hunting and gathering for sustenance. They hunted large game animals, such as mammoths, horses, and bison, and gathered wild plants, nuts, and berries. This subsistence strategy required complex social organization and cooperation within the community.
Middle Paleolithic Period: Shelter and Dwelling
Middle Paleolithic humans constructed temporary shelters, such as simple huts made of branches, leaves, and animal hides. These structures were protected from the elements and served as communal living spaces, emphasizing the importance of social bonds and cooperation for survival.
Symbolic Expression:
Artistic expressions and symbolic behavior emerged during the Middle Paleolithic period. Cave paintings, engravings, and personal adornments, such as beads and pendants made from shells or animal bones, suggest the development of symbolic communication and the expression of abstract thoughts and beliefs.
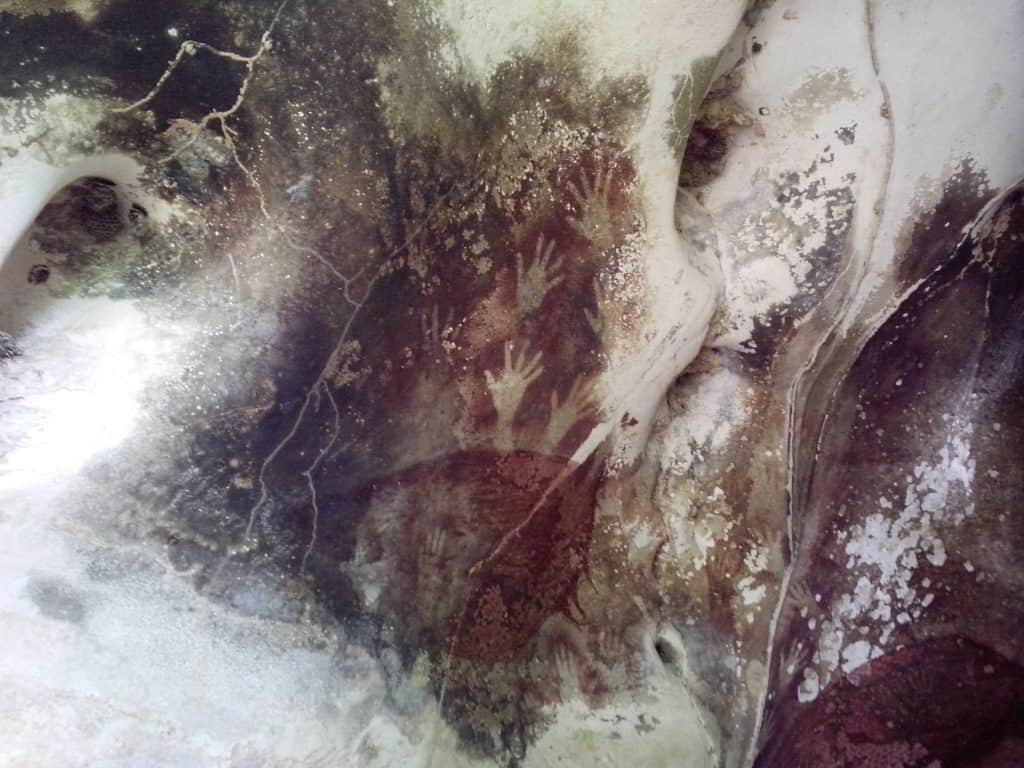
Credit: Cahyo, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Cultural Diversity:
During the Middle Paleolithic period, we see diverse cultural traditions and adaptations across different regions. Variations in tool technologies, artistic styles, and burial practices indicate distinct cultural groups with unique identities, beliefs, and social systems.
Evolutionary Significance:
The Middle Paleolithic period represents a crucial phase in human evolution, with Homo sapiens gradually emerging and Neanderthals flourishing across Europe and parts of Asia. The interactions and potential interbreeding between these hominin species have left a lasting genetic legacy in modern human populations.
The land of Israel boasts a treasure trove of Middle Paleolithic archaeological sites, providing valuable insights into the lives and activities of our ancient ancestors.
Carmel Caves: The Carmel Caves, located on the slopes of Mount Carmel, have revealed fascinating evidence of Middle Paleolithic habitation. Kebara Cave, for instance, yielded the discovery of a Neanderthal burial site, providing a rare glimpse into their burial practices and possible spiritual beliefs.
Nahal Me'arot Nature Reserve
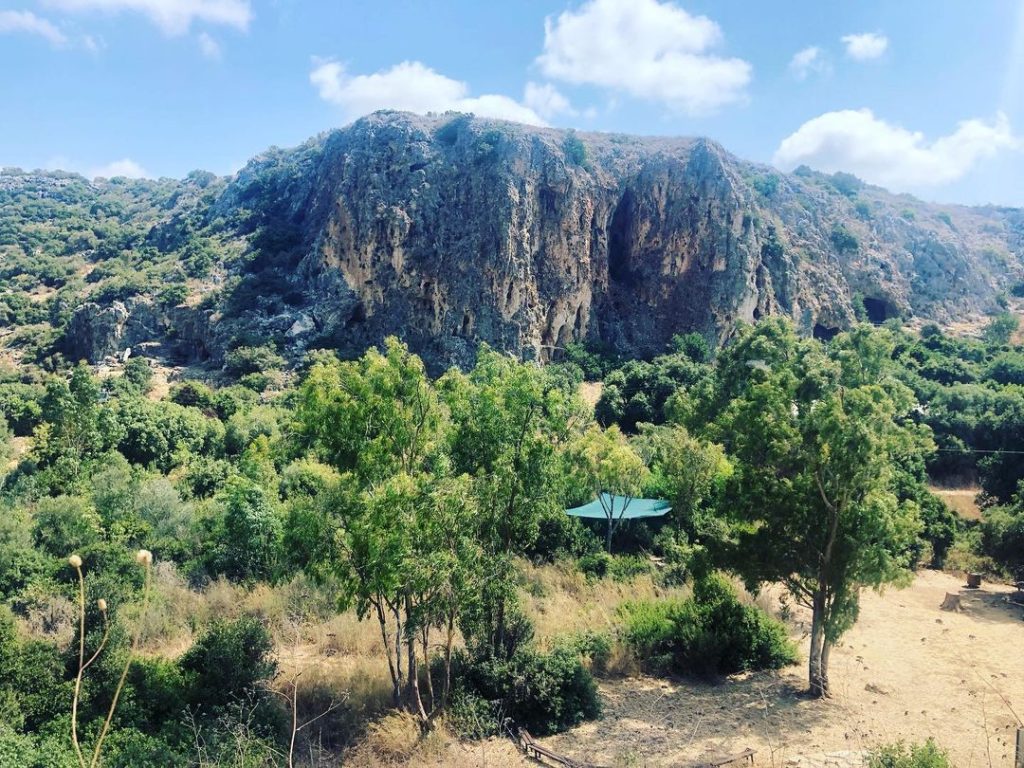

Qafzeh Cave: Situated near Nazareth, Qafzeh Cave has yielded crucial remains of early Homo sapiens. These discoveries, including human burials and cultural artifacts, provide invaluable information about our ancient human ancestors’ lifestyles and cultural practices.
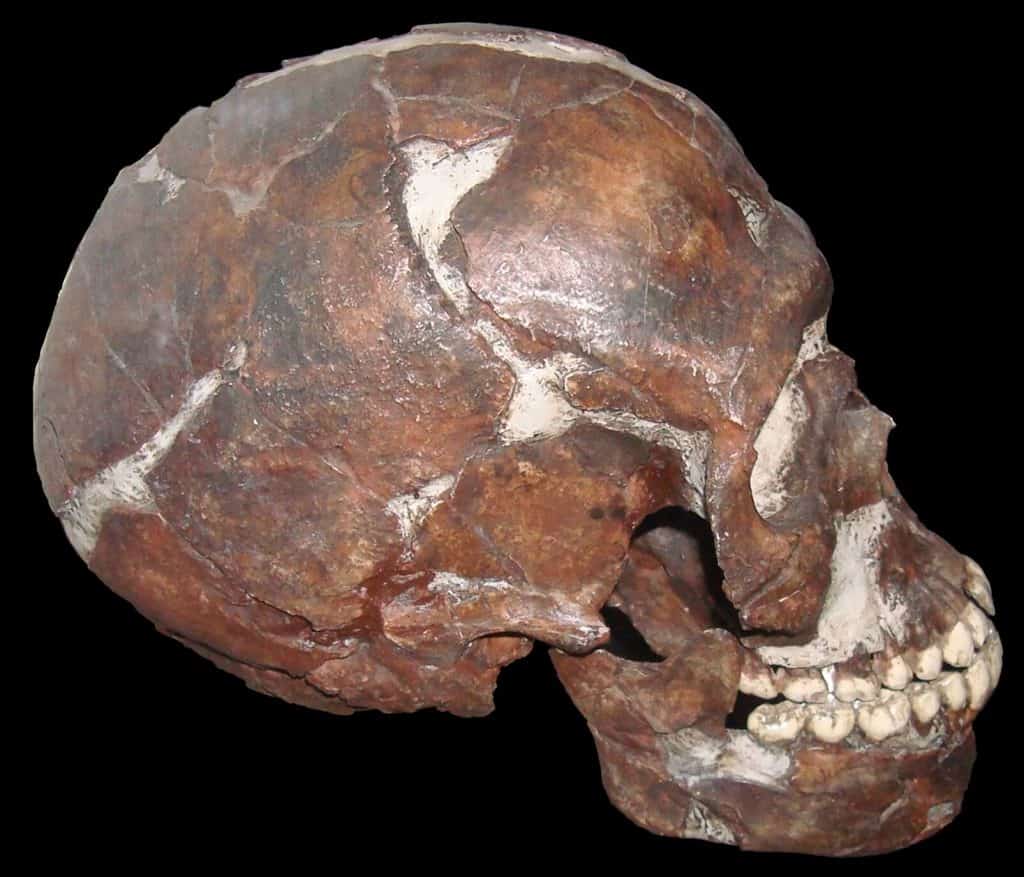
Credit: Wapondaponda, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Amud Cave: Amud Cave, found in the Upper Galilee region, has provided key insights into Neanderthal habitation. The cave contains evidence of their tool-making abilities, hunting practices, and adaptations to the local environment.
The Coastal Plain: The coastal plain of present-day Israel was also a significant area of Middle Paleolithic occupation—sites such as Geula Caves.
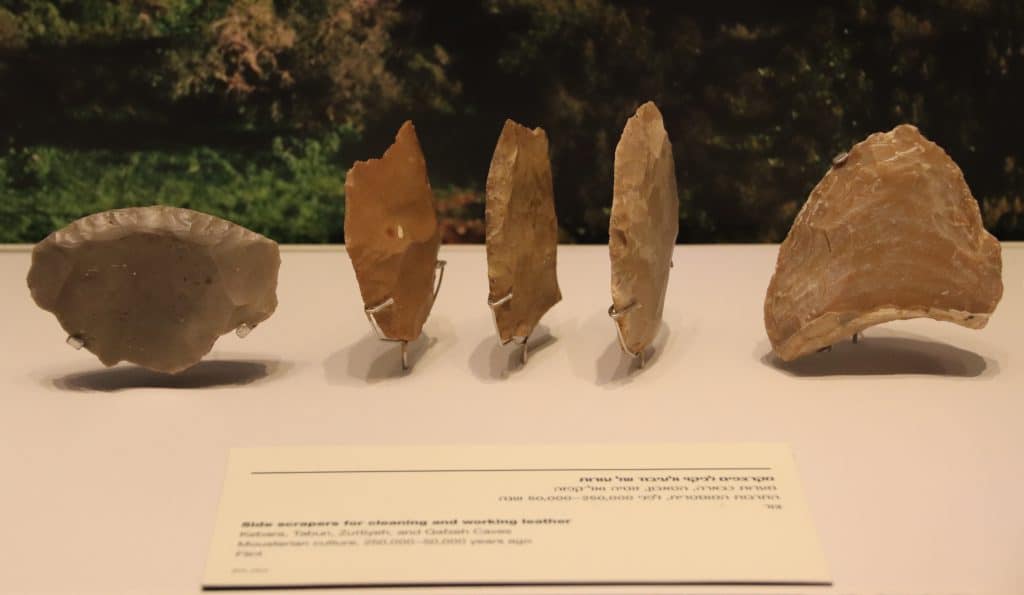

Preserving Our Ancient Heritage:
So the Middle Paleolithic period represents a crucial chapter in our human story, revealing our ancient ancestors’ remarkable adaptability, ingenuity, and cultural expressions. Exploring and understanding this period fosters a deeper appreciation for our shared evolutionary journey and the complex tapestry of human history.
Israel Museum Tour

Lastly, as we reflect on the Middle Paleolithic period, let us embrace the lessons it offers — the resilience, resourcefulness, and capacity for cultural expression demonstrated by our ancient human ancestors. May their enduring legacy inspire us to understand better and appreciate our diverse world and work toward a future of unity, cooperation, and progress.

