Legio X Fretensis (“Tenth legion of the Strait”) was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was founded by the young Gaius Octavius (later to become Augustus Caesar) in 41/40 BCE to fight during the period of civil war that started the dissolution of the Roman Republic. X Fretensis is then recorded to have existed at least until the 410s. Legio X Fretensis symbols were the bull. Which is the holy animal of the goddess Venus (mythical ancestor of the gens Julia). And a ship (probably a reference to the Battles of Naulochus and/or Actium); the god Neptune, and a boar. The symbol of Taurus may also mean that it was organized between 20 April and 20 May.

Octavian, later known as Augustus; levied a legion and gave it the number ten; as a reference to Julius Caesar’s famous Tenth Legion. In 36 BCE, the Tenth Legion fought under Octavian against Sextus Pompey in the Battle of Naulochus; where it earned its cognomen Fretensis. The name refers to the battle taking place near the sea Strait of Messina (Fretum Siculum).

In 31 BCE, it fought in the Battle of Actium against Mark Antony. Although Actium was a battle at sea; the legion was able to board enemy ships that had been hooked close by means of an iron grapnel known as the Corvus. Its key participation in this battle is probably the reason that the legion also used a trireme as one of its symbols. Actium marked the end of the civil war and the rise to power of Octavian; who has proclaimed Augustus some years later.

Legio X Fretensis Suppress the First Jewish-Roman War
X Fretensis was centrally involved in the First Jewish-Roman War (66–73); under the supreme command of Vespasian. In 66, the X Fretensis and V Macedonica went to Alexandria for an invasion of Ethiopia planned by Nero. However, the two legions were needed in Judaea to suppress a revolt.

After spending the winter in Ptolemais Ace (modern Acre, Israel); Legio X Fretensis and V Macedonica relocated to the coastal city of Caesarea Maritima (67/68CE). This was due to the large number of legions being mobilized in Ptolemais; under Marcus Ulpius Traianus; the future governor of Syria; and the father of the emperor Trajan. During that same winter, the Caesarea camp of Xth and Vth hosted Vespasian; who was forced to go to Rome the following year, where he seized power; Vespasian’s son Titus finished the suppression of the revolt.

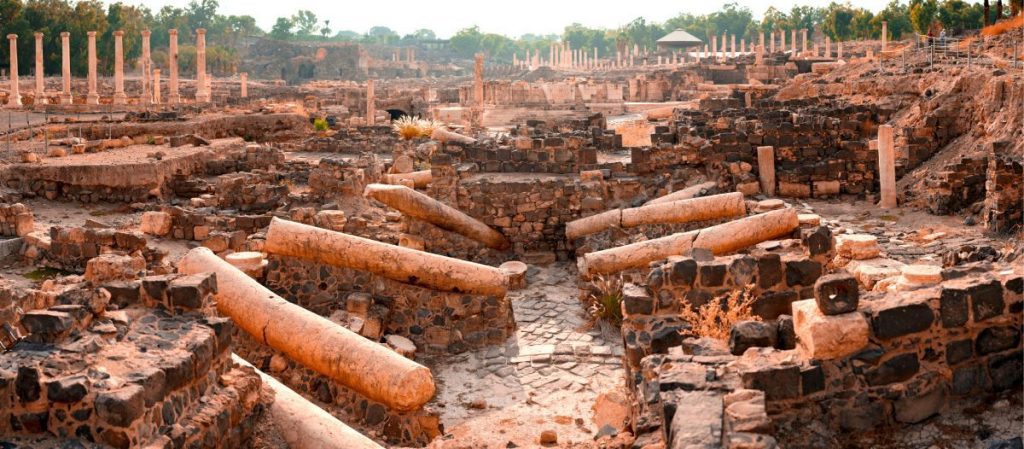
When Tarichacae and Gamla were conquered, the Legio X Fretensis moved to Scythopolis (Beit Shean); just west of the Jordan River. In the summer of 68CE; Legio X Fretensis destroyed the monastery of Qumran; where the Dead Sea Scrolls are believed to have originated. Its winter camp was at Jericho.

The Destruction of Jerusalem
By 70, the rebellion in all of Judaea had been crushed, except for Jerusalem and a few fortresses, including Masada. In that year Legio X Fretensis, in conjunction with V Macedonica; XII Fulminata, and XV Apollinaris began the siege of Jerusalem; the stronghold of the rebellion. The Xth camped on the Mount of Olives. During the siege, Legio X gained fame in the effective use of their various war machines.
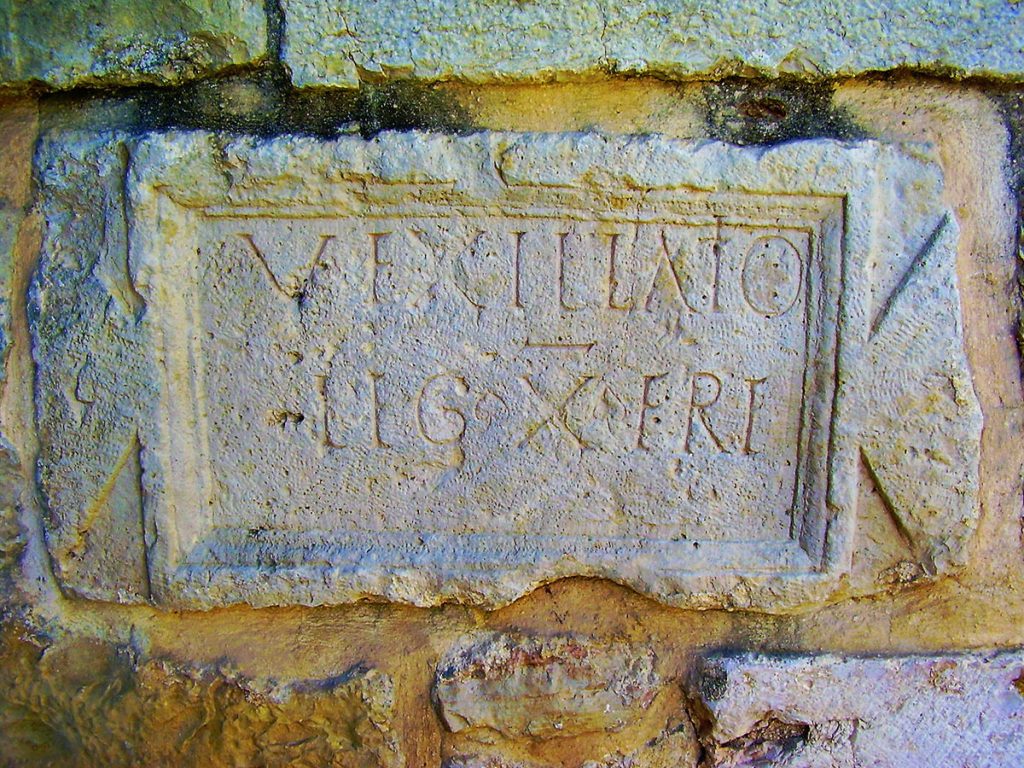
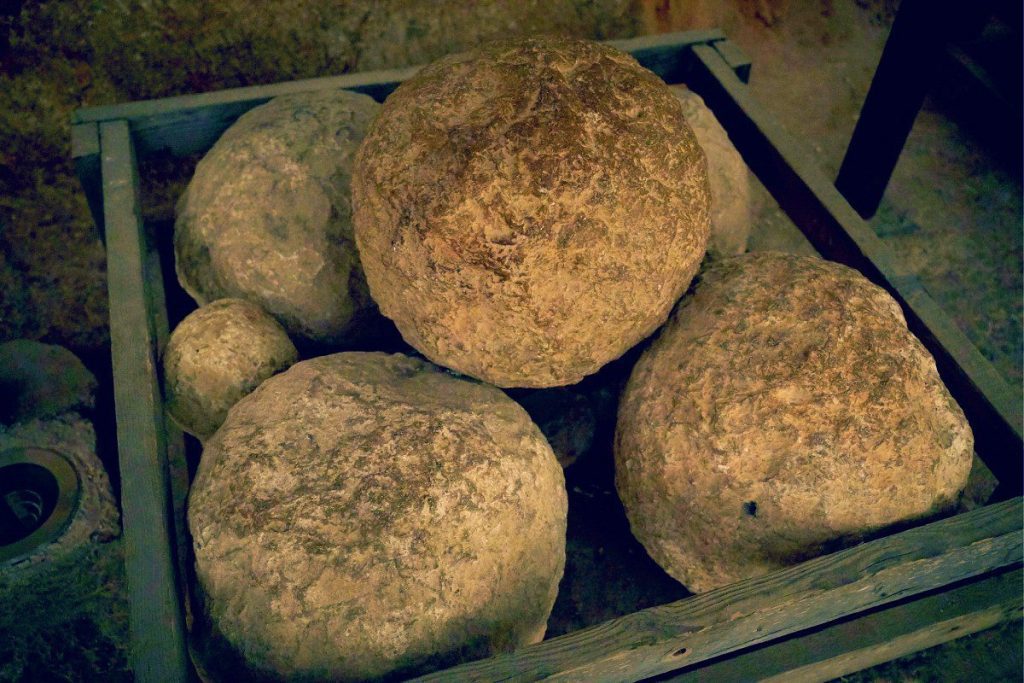
It was noted that they were able to hurl stones that weighted a talent (about 25 kg) a distance of two furlongs (400 m) or further. The projectiles of their ballistae caused heavy damage to the ramparts. According to Josephus Larcius Lepidus was the commanding officer of the Roman X Legion. The siege of Jerusalem lasted five months and the besieged population experienced all the terrible rigors of starvation. Finally, the combined assaults of the legions succeeded in taking the city; which was then subjected to destruction.
The Siege at Masada
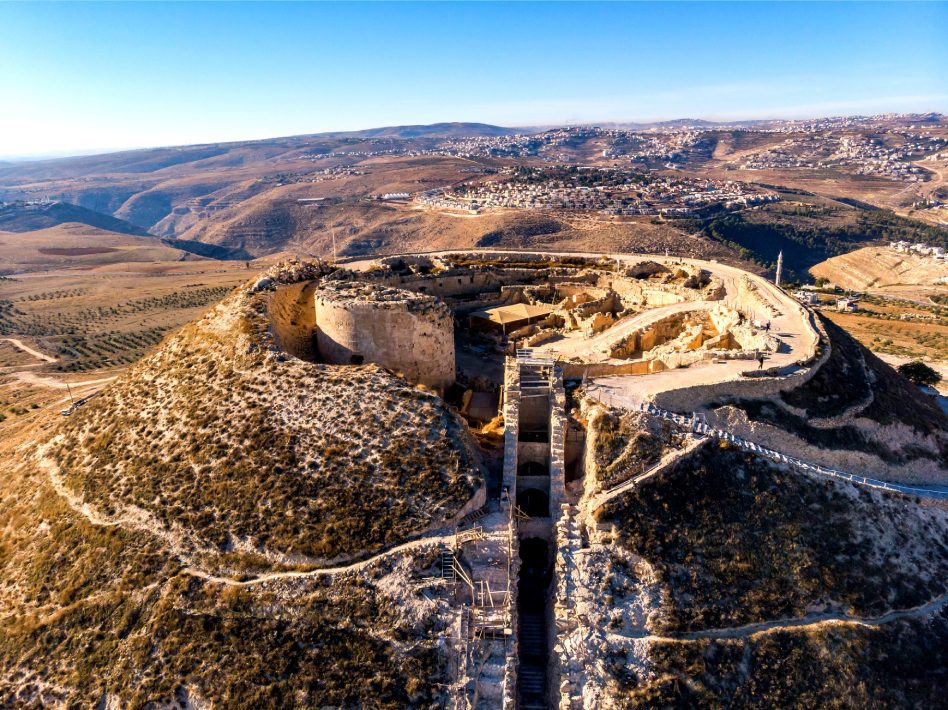
During the spring of 71CE, Titus set sail for Rome. A new military governor was then appointed from Rome; Sextus Lucilius Bassus; whose assigned task was to undertake the “mopping-up” operations in Judaea. Naturally, he used Legio X Fretensis to oppose the few remaining fortresses that still resisted. As part of this, X Fretensis took Herodium and then crossed the Jordan to capture the fortress of Machaerus on the shore of the Dead Sea.
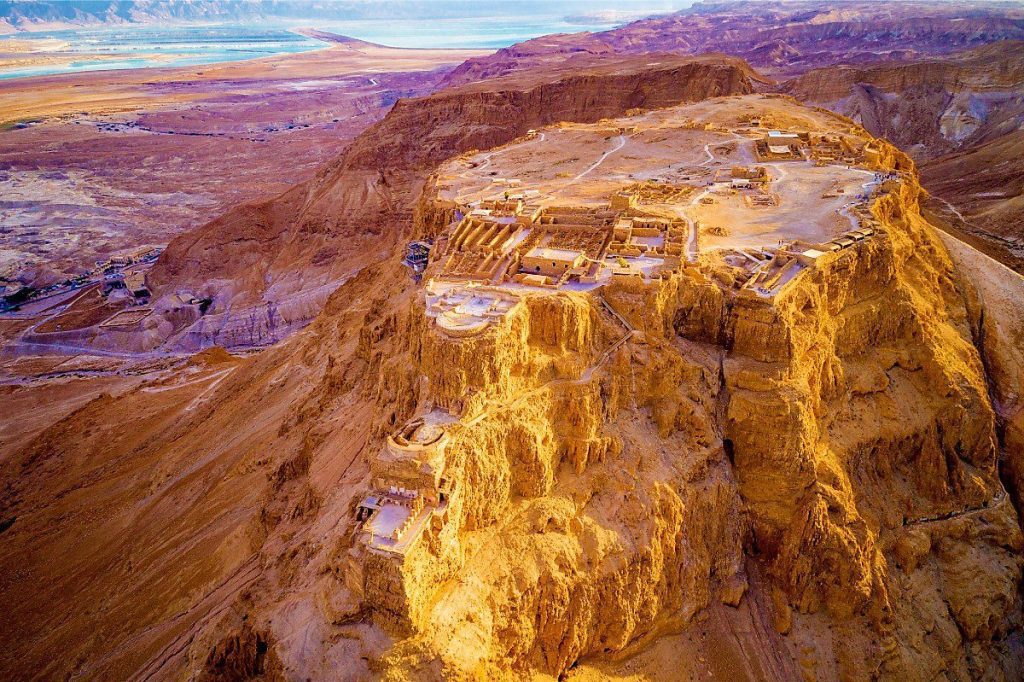

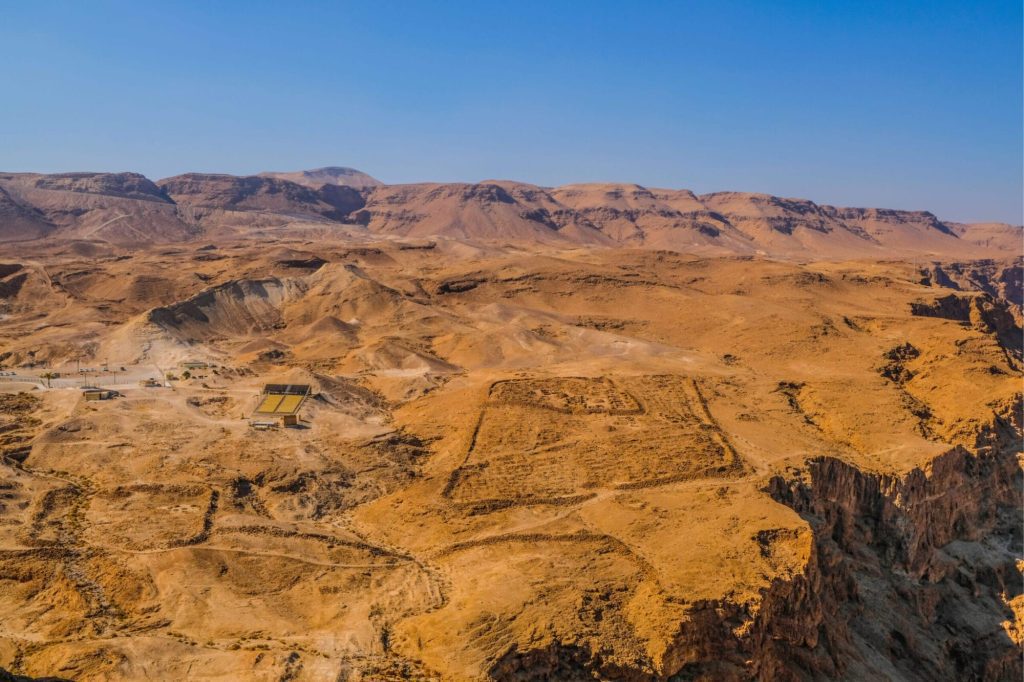
Due to illness, Bassus did not live to complete his mission. Lucius Flavius Silva replaced him, and moved against the last Jewish stronghold, Masada, probably in the autumn of 72. He used Legio X Fretensis, auxiliary troops, and thousands of Jewish prisoners. After his orders for surrender were rejected, Silva established several base camps and a wall of circumvallation completely around the fortress. When the Romans finally broke through the walls of this citadel; they discovered that the Jewish defenders had chosen death with a mass suicide.
Legio X Fretensis is Garrisoned at Jerusalem
After the conclusion of the Jewish revolt, Legio X Fretensis was garrisoned at Jerusalem. Their main camp was positioned on the Western Hill; located in the southern half of what is now the Old City; which had been leveled off all former buildings. The camp of the Tenth was built using the surviving portions of the walls of Herod’s royal palace; demolished by order of Titus. Once the Romans rebuilt parts of the destroyed city as the pagan city of Aelia Capitolina, the camp found itself at the end of the Cardo Maximus.

At the time, Legio X was the sole legion assigned to maintain the peace in Judaea and was directly under the command of the governor of the province, who was also legatus of the legion. his combination of offices made this posting important, and several of the men assigned to it had previous experience commanding a legion. However, when a second legion was assigned to Judaea; and the province was promoted to consular status; the political status of the legate of this legion declined.
Bar Kokhba Revolt
After participating in Trajan’s Parthian campaign, Legio X Fretensis was caught up in the Bar Kokhba’s revolt (132-135). A possible cause for the revolt was the decision of Emperor Hadrian to build a pagan temple to Jupiter in Jerusalem. Simon Bar Kokhba started the revolt and inflicted massive casualties on the Romans. The war ended when the Roman army — including Legio X Fretensis and Danubian troops under the command of Sextus Julius Severus — reconquered the entire territory and successfully besieged the last Jewish stronghold, the fortress of Betar. Legio X Fretensis sustained heavy casualties in the course of the revolt. As a consequence of the unrest in the region, Fretensis was supported by several other legions, of which the Legio VI Ferrata was stationed at a camp which became known as Lejjun (from “legion”).

Later History of the Tenth Roman Legion
A vexillation, or detachment, of X Fretensis along with other troops stationed in eastern provinces, fought in the Marcomannic campaign of Marcus Aurelius. However, when this vexillation arrived or what part it played in the campaign is not known. In 193, the legion supported Pescennius Niger against Septimius Severus and was possibly involved in a local struggle between Jews and Samaritans. The legion was still in Jerusalem at the time of Caracalla (r. 211–217) or Elagabalus (r. 218–222).

Under Gallienus (r. 253–268), another vexillation of Fretensis was drawn to fight in the war against the Gallic Empire. However, that unit defected to the other side. The legion moved to Aila (close to modern Aqaba), probably during Diocletian’s reforms (around 300); and is recorded as still camping there at the time of the compilation of the Notitia Dignitatum in the 390s; when it is reported serving under the Dux Palaestinae.
Legio X Fretensis: Archaeology
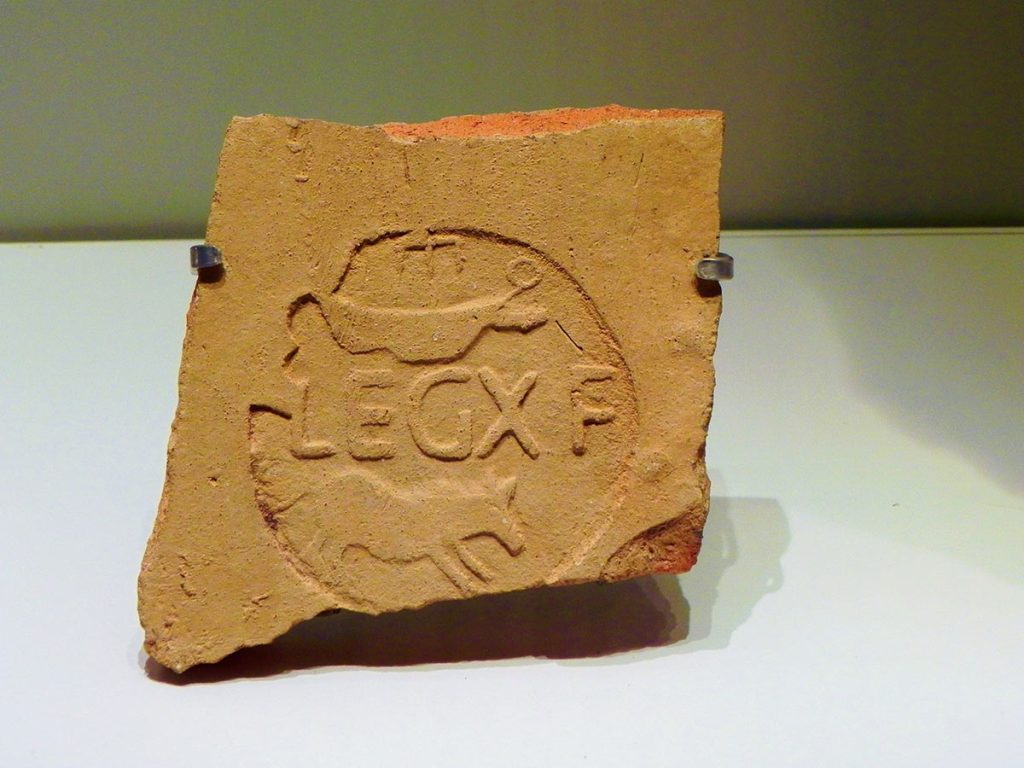
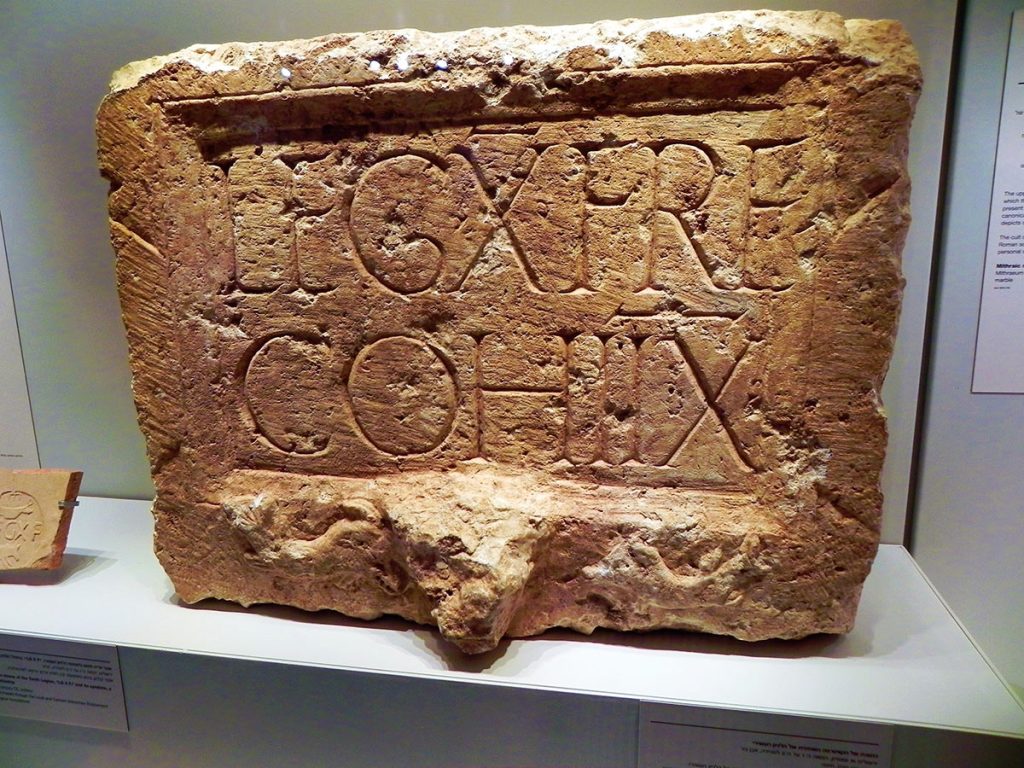
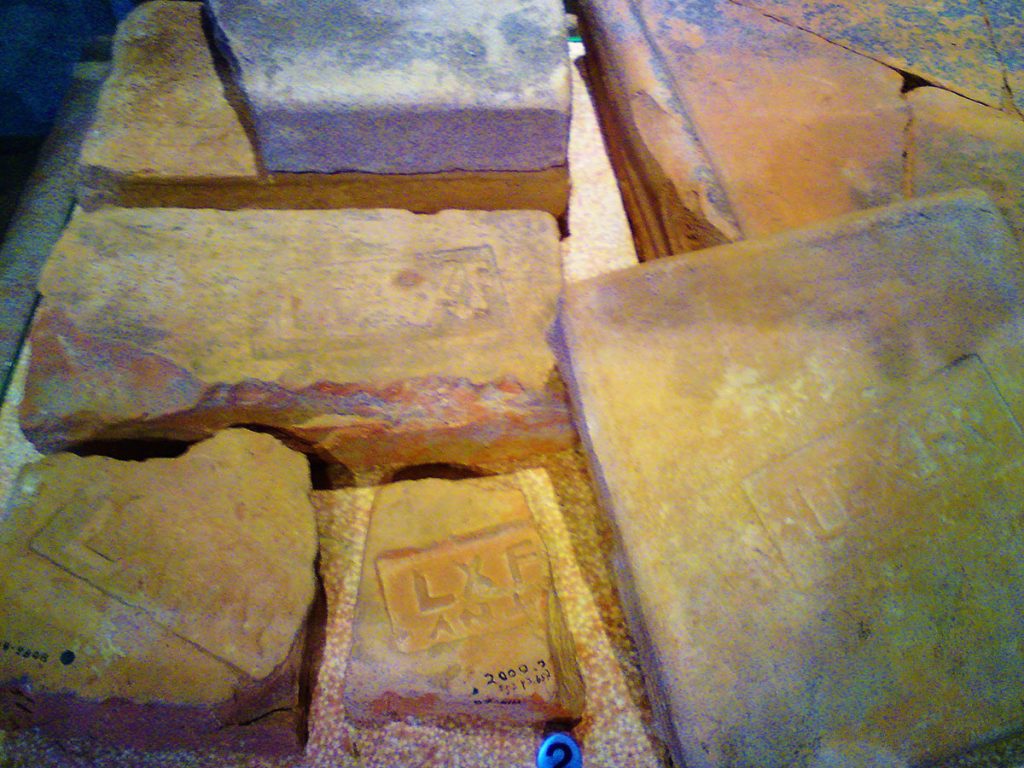
Some fragments bearing the “L.X.F” mark of the Legio X Fretensis are present at the Tower of David in Jerusalem. Roman Law required all pottery to bear the maker’s stamp, and the Legion pottery works just to the West of Jerusalem were obviously no exception. A huge production of pottery bearing the marks of the Legio X Fretensis has been discovered in Jerusalem. The mark “LE X FR” was also used in the pottery of the Legion.
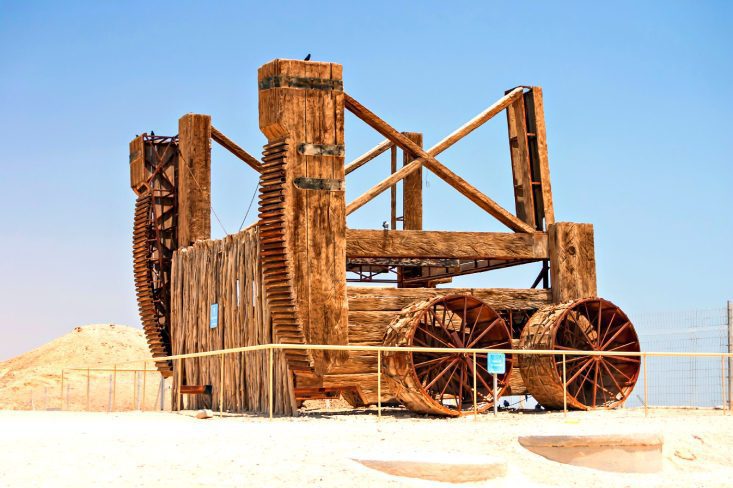

Where can we see some of the traces of the Roman Tenth Legion? In Jerusalem, for sure, there is lots of evidence for the presence of the Legion. Of course, in Masada, you can still see the well-preserved siege system constructed by the Legio X Fretensis, including the Roman siege camps and Roman Ramp. Also, in Caesarea, inscriptions of the Legion were found; since they were the ones preparing the aqueduct in times of peace.







