The story of human evolution is a captivating journey that spans millions of years. At the heart of this epic narrative lies the Australopithecus, a group of extinct hominins that played a crucial role in shaping the early stages of human development. In this post, we explore the fascinating world of Australopithecus, unlocking the mysteries of our ancient ancestors.
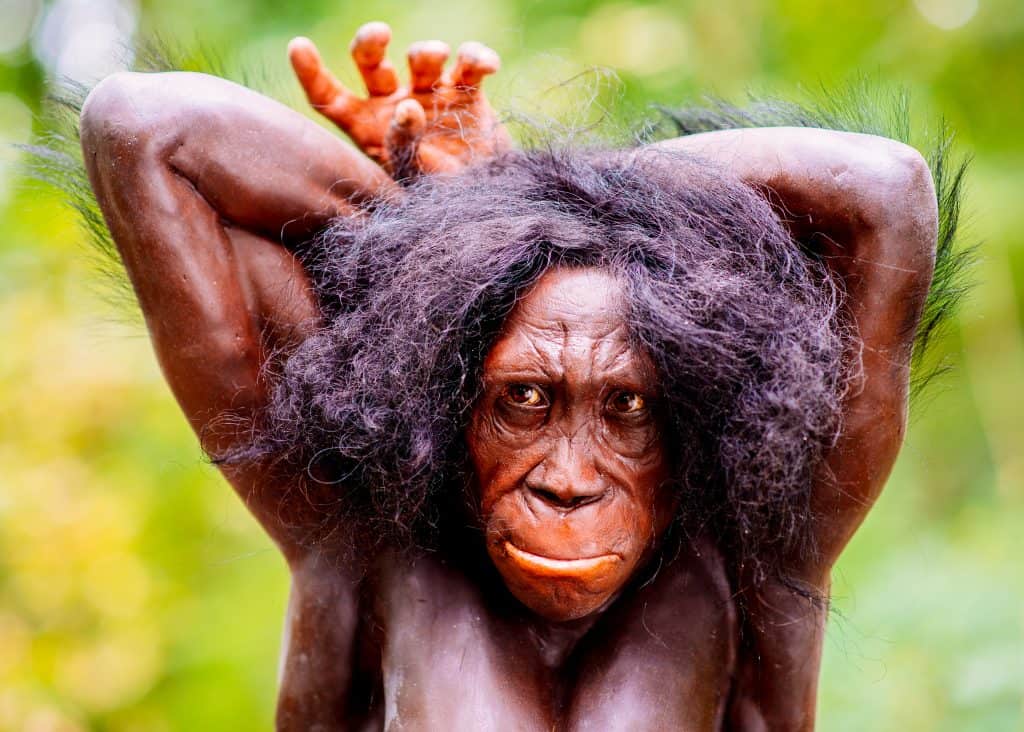

Credit: Neanderthal-Museum, Mettmann, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
So the Australopithecus is a genus of bipedal primates that lived in Africa between 4.2 and 2 million years ago during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs. These hominins marked an essential milestone in the evolutionary pathway towards modern humans. While not direct ancestors of Homo sapiens, Australopithecus species are considered our distant relatives and share a common ancestor.
Physical Characteristics
Australopithecus species exhibited a combination of ape-like and human-like characteristics. Furthermore, They were bipedal, meaning they walked on two legs, but also retained some traits adapted for tree climbing. In addition, they had relatively small brains compared to modern humans and prominent jaws with enormous teeth adjusted to a mixed diet of fruits, nuts, seeds, and possibly some meat.
Fossil Discoveries
One of the most significant fossil discoveries that brought Australopithecus to the forefront was “Lucy” (Australopithecus afarensis), found in Ethiopia in 1974. Lucy’s remarkably preserved skeleton provided valuable insights into these early hominins’ physical structure and locomotion. Moreover, the “Taung Child” (Australopithecus africanus) discovered in South Africa in 1924 contributed crucial evidence to studying human evolution.
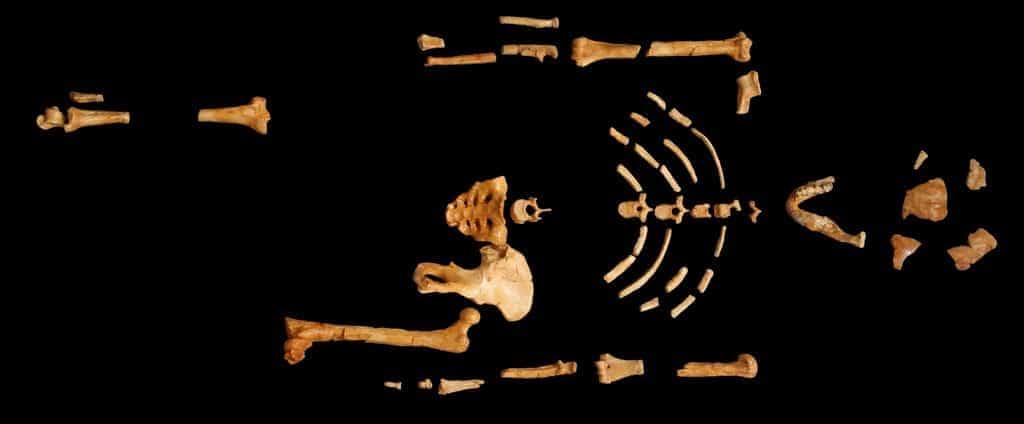
Credit: 120, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Bipedalism and Adaptive Advantages
The evolution of bipedalism was a pivotal adaptation for Australopithecus. Walking upright allowed them to traverse open landscapes and access new food resources efficiently. Bipedalism also freed their hands for tool use, food gathering, and caregiving, laying the groundwork for further advancements in human evolution.
The Lower Paleolithic

Social Organization
Australopithecus likely lived in social groups, as evidence from fossil footprints indicates that they moved in groups or families. Their social structures may have influenced their cooperation, communication, and problem-solving abilities, contributing to the development of early human societies.
Credit: Kameraad Pjotr & Sting, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Conclusion
Last, the Australopithecus represents a remarkable chapter in the human evolutionary story. These early hominins paved the way for the emergence of our genus, Homo, and played a critical role in shaping the course of human evolution. Through their bipedalism and adaptive strategies, Australopithecus expanded their ecological niche and set the stage for the eventual rise of modern humans.
Ultimately, studying Australopithecus provides profound insights into our ancestral roots, shedding light on the evolutionary journey that led to our complex and diverse species. As the search for more fossil evidence continues, we remain humbled and intrigued by the rich tapestry of human evolution, forever connected to these ancient beings that once roamed the ancient African landscapes.

