The 2006 Lebanon War, also known as the Second Lebanon War, was a significant armed conflict between Israel and Lebanon in the summer of 2006. Characterized by intense military operations and civilian casualties, this war profoundly impacted both countries and further exacerbated regional tensions. This post delves into the key events, underlying factors, and lasting consequences of the 2006 Lebanon War.

Credit: Israel Defense Forces, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
So the roots of the 2006 Lebanon War can be traced back to the longstanding enmity between Israel and Lebanon, compounded by the presence of Hezbollah, a Shiite Islamist militant and political group based in Lebanon. Hezbollah’s capture of two Israeli soldiers in a cross-border raid on July 12, 2006, catalyzed the outbreak of the conflict.
2006 Lebanon War: Hezbollah’s Role
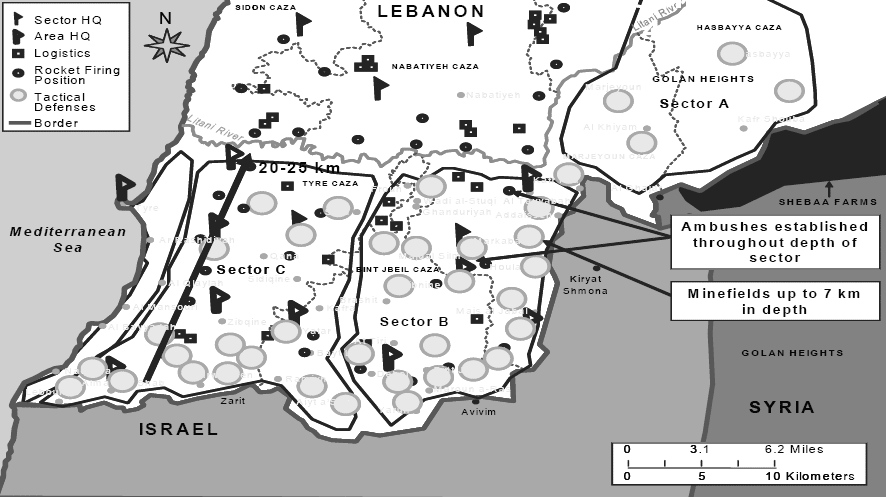
No doubt, Hezbollah’s involvement in the war was significant. The group, equipped with rockets and well-prepared underground bunkers, launched a barrage of attacks on northern Israel, targeting civilian areas. Using guerrilla tactics and hidden rocket launchers presented considerable challenges for Israel’s military response.
Israel’s Response
So, as a result, Israel launched a large-scale military offensive in Lebanon in response to Hezbollah’s attacks. The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) conducted airstrikes on Hezbollah strongholds, infrastructure, and areas suspected of housing weapons caches and launchers. The IDF also imposed a naval blockade to prevent the delivery of arms to Hezbollah.
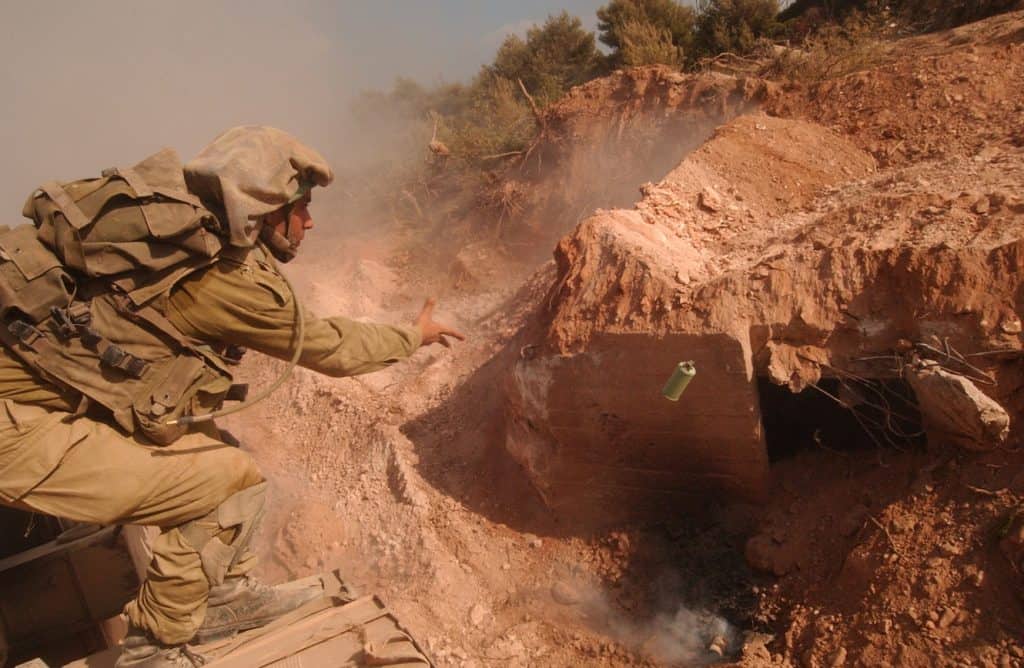

Credit: Israel Defense Forces, CC BY 2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
2006 Lebanon War: Impact on Lebanon
The 2006 Lebanon War devastated Lebanon’s civilian population. The intense Israeli airstrikes resulted in numerous civilian casualties and extensive damage to civilian infrastructure, including homes, schools, and hospitals. The war displaced thousands of Lebanese civilians, creating a urgent humanitarian crisis.
International Involvement
The conflict garnered significant international attention and engagement. The United Nations and other countries played a crucial role in attempting to broker a ceasefire and negotiate an end to the hostilities. On August 14, 2006, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 1701, which called for an immediate cessation of hostilities and the deployment of UN peacekeeping forces to the Lebanon-Israel border.
1982 Lebanon War
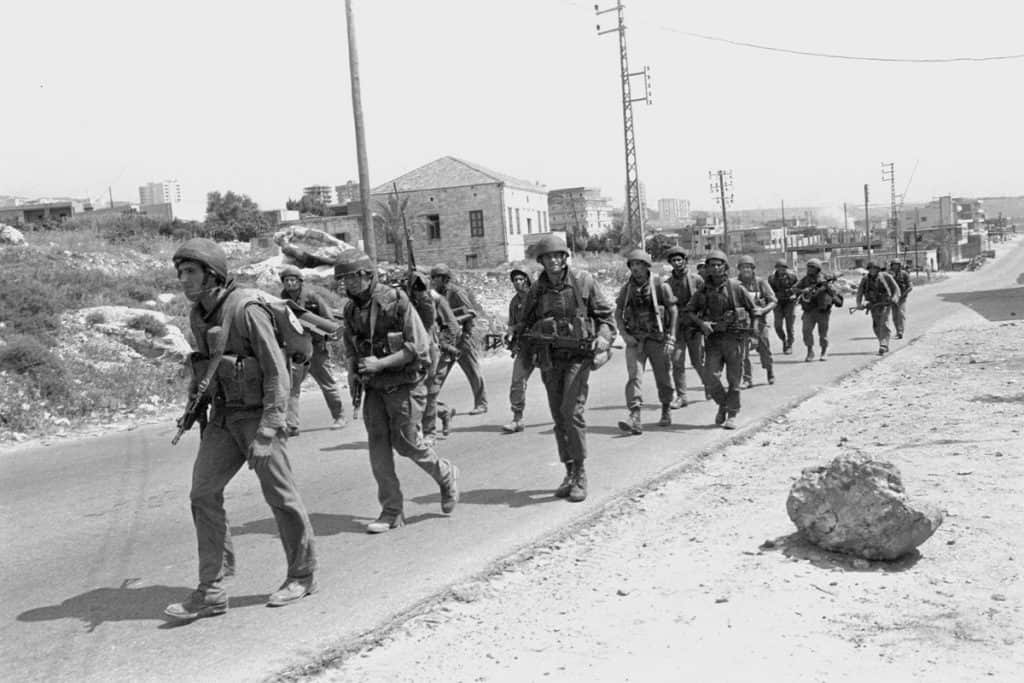

Consequences and Aftermath
So, the war ended with a fragile ceasefire, but its impact reverberated in the region. Lebanon faced the arduous task of rebuilding and recovering from the devastation caused by the conflict. Moreover, the war also showcased the limitations of military force in dealing with non-state actors like Hezbollah, prompting Israel to reevaluate its security strategies.
The Legacy
No doubt, The 2006 Lebanon War had a lasting impact on Lebanon and Israel. Furthermore, the conflict exposed the vulnerabilities of civilian populations in times of war and underscored the importance of pursuing peaceful resolutions to longstanding regional disputes.
The Wars of the State of Israel

Credit: Itayba On Hebrew Wikipedia, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Conclusion
Last, the 2006 Lebanon War remains a stark reminder of the complexities and ramifications of armed conflicts in the Middle East. Its devastating toll on civilians underscores the urgency of seeking diplomatic solutions to regional tensions and conflicts. Furthermore, as the region grapples with geopolitical challenges, understanding the events and lessons of the 2006 Lebanon War remains crucial in fostering lasting peace and stability for all parties involved.

