Nestled within the Carmel mountain range in Israel, Es Skhul Cave is an archaeological marvel crucial in shedding light on prehistoric human life. This ancient cave has been the site of groundbreaking discoveries, revealing vital information about early human populations’ lifestyles, behaviors, and cultural practices. In this post, we explore the significance of Es Skhul Cave to prehistoric research and its contributions to our understanding of human evolution.
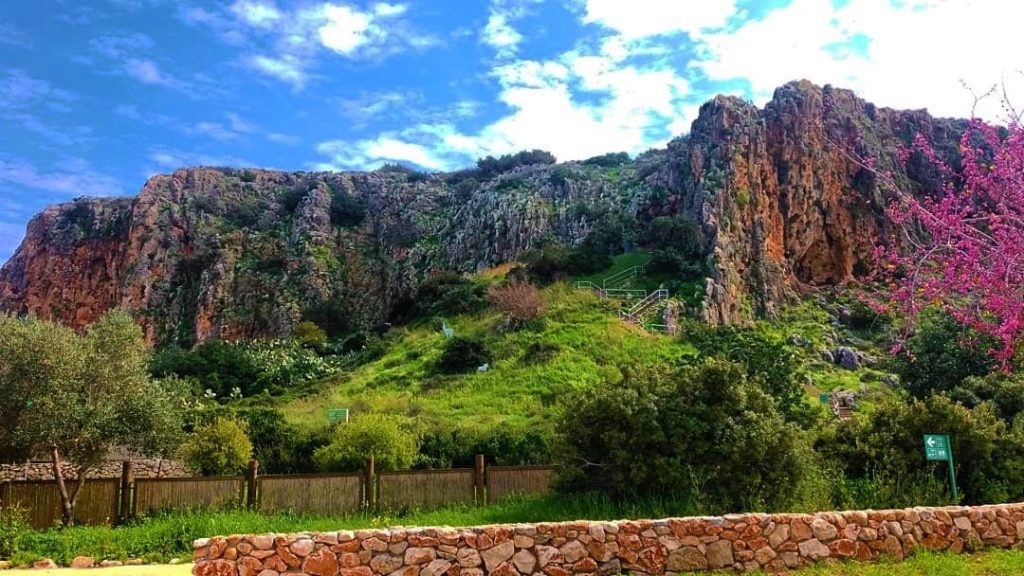

First, Es Skhul Cave was excavated in the 1930s by Dorothy Garrod, a pioneering archaeologist. The cave’s name, “Es Skhul,” is derived from the Arabic word for “the place of the dogs,” possibly due to the presence of wild canines in the area during ancient times.
In addition, Skhul Cave, along with the adjacent sites of Tabun Cave, Jamal Cave, and the cave at El Wad, forms an integral part of the Nahal Me’arot Nature Reserve. This renowned reserve holds national park status and is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
A Prehistoric Time Capsule
Furthermore, the stratified layers of sediment in Es Skhul Cave have preserved a rich archaeological record spanning hundreds of thousands of years. Moreover, the remains of various animal species and stone tools found in the cave have provided valuable insights into the lives of early humans who inhabited the region during the Middle and Upper Paleolithic periods.
Evidence of Early Human Occupation
The excavation at Es Skhul Cave revealed the presence of early Homo sapiens, known as anatomically modern humans. Furthermore, the discovery of fossilized human remains, including skulls and bones, has provided significant evidence of human occupation in the region dating back more than 100,000 years.
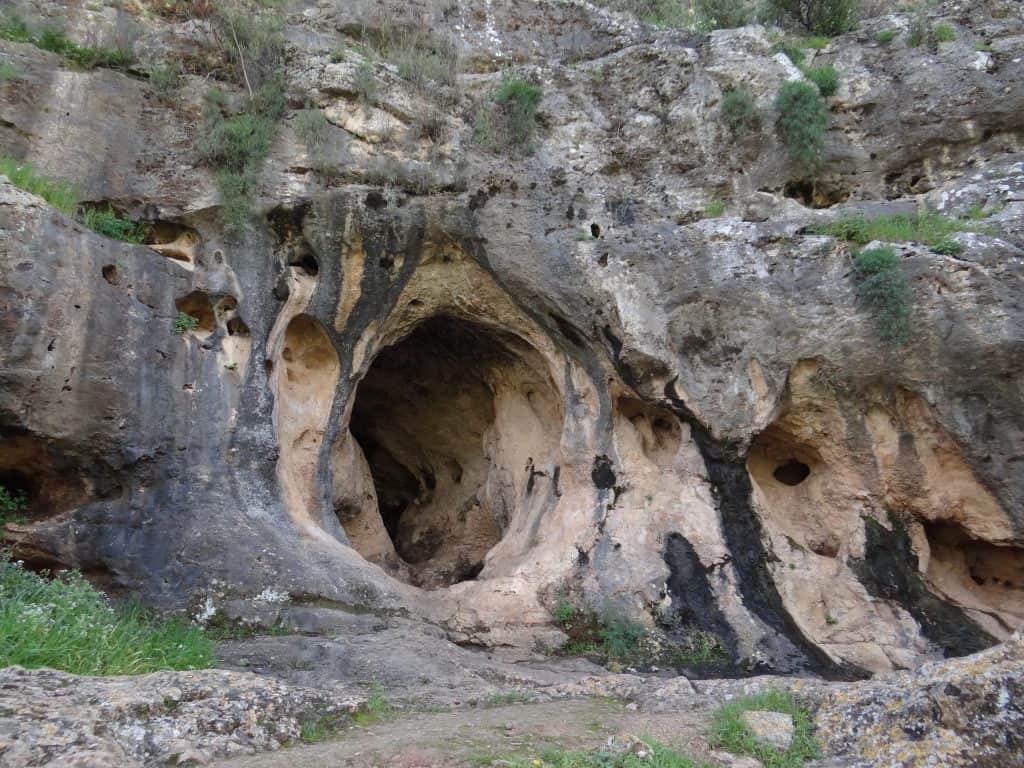

Credit: Hanay, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Interglacial Periods and Climate Change
The archaeological findings from Es Skhul Cave have offered clues about the climate fluctuations that early humans experienced during the interglacial periods of the Pleistocene epoch. Analysis of animal remains and plant materials has provided valuable data about the area’s environmental conditions and resource availability.
The Cultural Practices at Es Skhul Cave
So the artifacts discovered at Es Skhul Cave, such as stone tools and personal ornaments, provide glimpses into prehistoric humans’ cultural practices and technological abilities. The presence of burial sites and evidence of early symbolic expression suggests the existence of rudimentary rituals and burial traditions.
Upper Paleolithic Period

Evidence of Human Interaction
The coexistence of various animal species within the cave environment, including humans, offers intriguing insights into the ecological dynamics and human interactions with the surrounding fauna. Such evidence aids researchers in understanding how early humans adapted and survived in their environment.
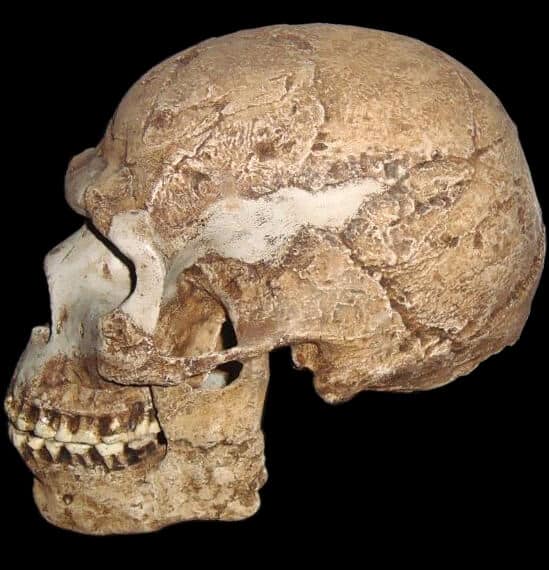
Credit: Wapondaponda, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Contributions to Human Evolutionary Studies
So Es Skhul Cave’s archaeological findings have significantly contributed to studying human evolution. By analyzing the ancient human remains and comparing them with other fossils from different regions, scientists have gained valuable data to reconstruct the intricate journey of human dispersal and adaptation.
Conclusion
So Es Skhul Cave in the Carmel mountain range holds a special place in prehistoric research, providing a unique window into the lives of early humans and their cultural practices. Furthermore, the cave has offered valuable insights into human evolution, adaptation, and environmental interactions through its rich archaeological record and fossil remains. In Short, as scientists continue to explore this archaeological marvel, Es Skhul Cave will undoubtedly reveal further mysteries and add to our ever-evolving understanding of our ancient human past.

