Welcome to the enthralling world of the Upper Paleolithic period, a remarkable chapter in human history filled with cultural and technological advancements. Join me on a captivating journey as we explore the rich tapestry of this transformative era, where our ancient human ancestors left an indelible mark on the landscape of our past.
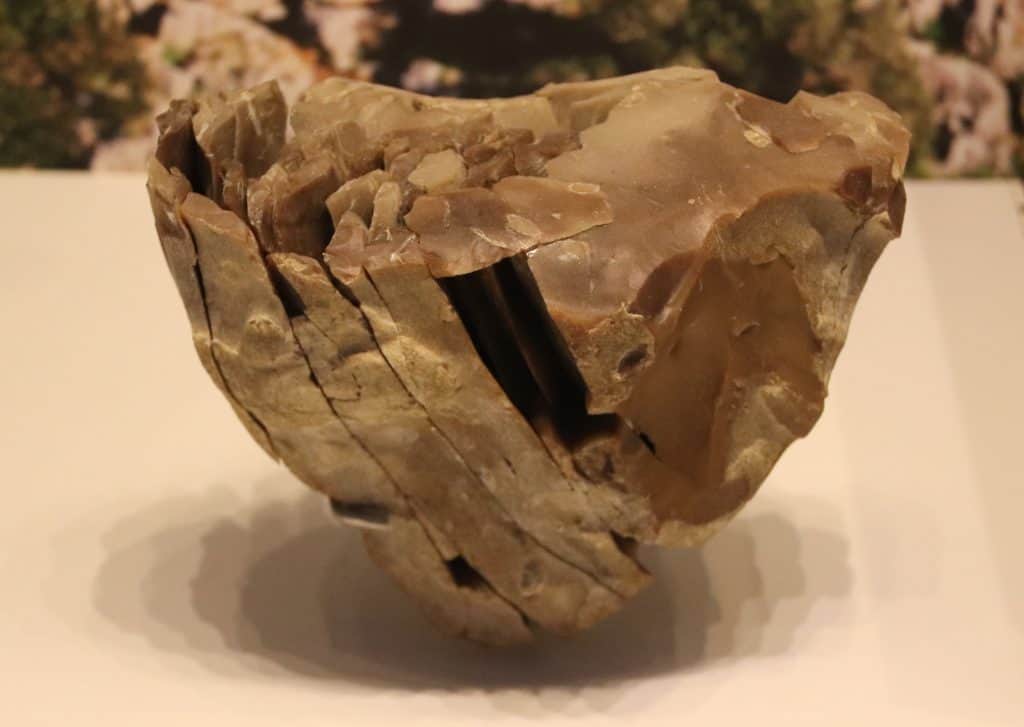

The Upper Paleolithic period, spanning from approximately 50,000 to 10,000 years ago, marked a pivotal time in human development. It witnessed the emergence and spread of Homo sapiens (modern humans) across different regions, laying the foundation for the diverse cultures and societies that would flourish in later epochs.
The Upper Paleolithic period unfolded across various parts of the globe, including Africa, Europe, Asia, and the Americas. It is a testament to the adaptability and resilience of our ancestors as they ventured into diverse environments, ranging from frigid tundras to lush forests and arid plains.
The Upper Paleolithic Period: An Artistic Renaissance:
One of the hallmarks of the Upper Paleolithic period was an unprecedented explosion of artistic expression. Our ancient ancestors displayed remarkable creativity and skill through cave paintings, engravings, sculptures, and personal adornments. These masterpieces depicted intricate details of animals, humans, and abstract symbols, offering glimpses into their spiritual beliefs, mythologies, and cultural practices.
Middle Paleolithic Period
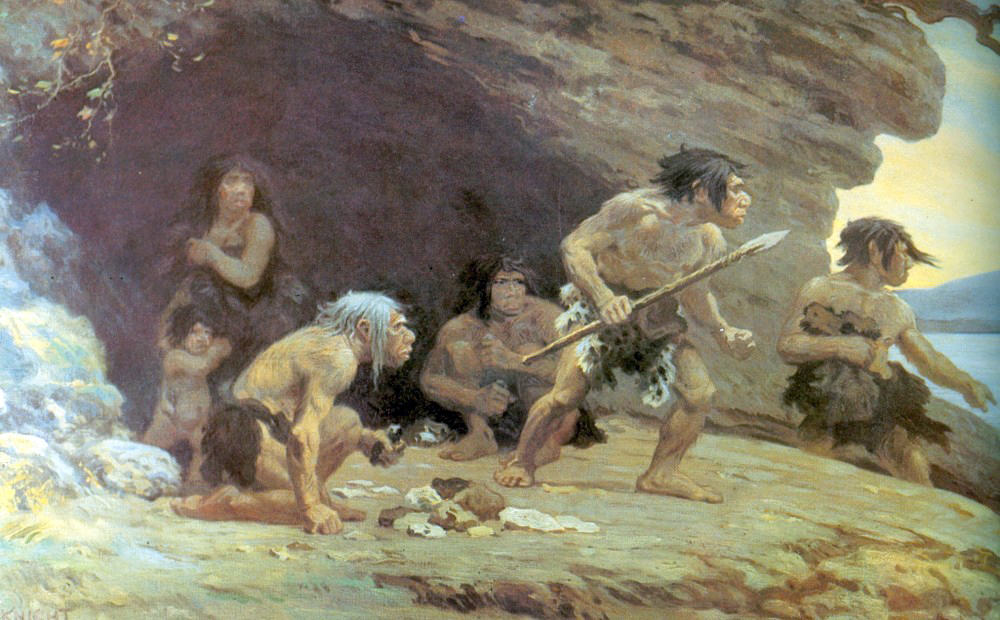

Technological Marvels:
In the land of Israel, the Upper Paleolithic period, they witnessed impressive advancements in tool-making techniques. Our ancestors developed refined stone shape methods, creating finely crafted blades, burins, and other tools. These technological innovations facilitated hunting, food processing, and other resource-intensive activities, enhancing their survival and adaptability.
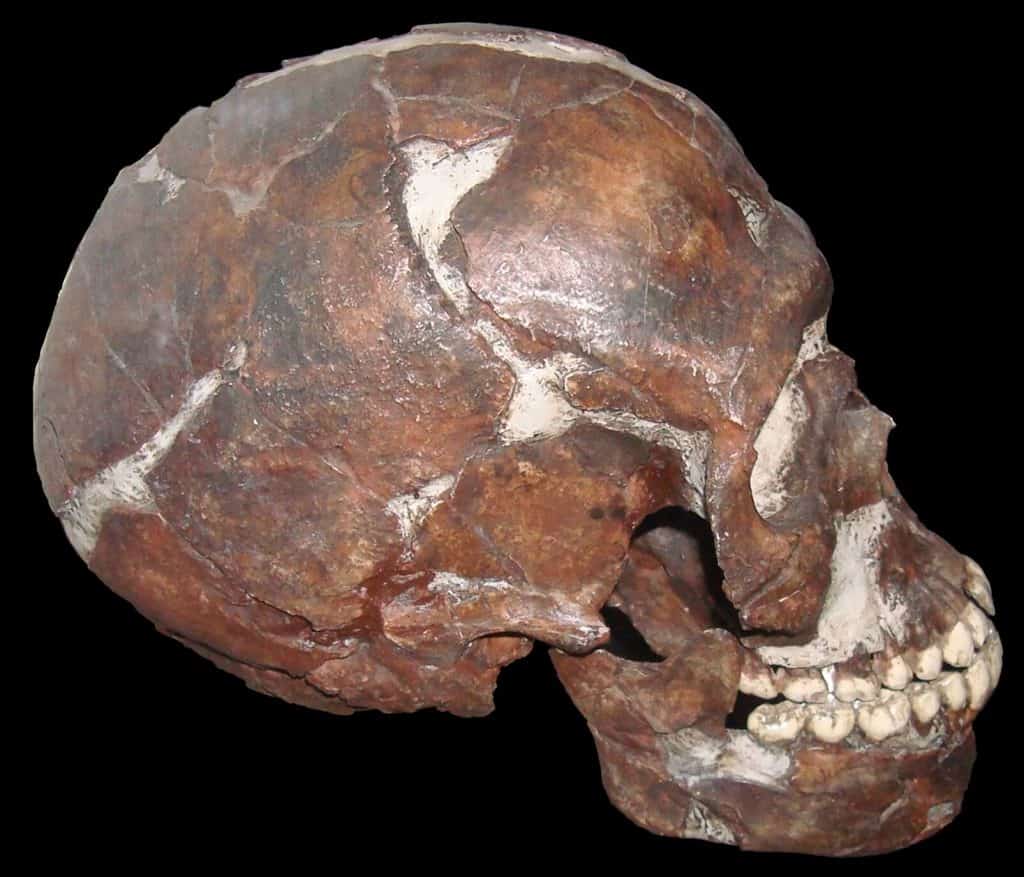
Credit: Wapondaponda, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons.
Cultural Complexity and Social Dynamics:
Intricate social structures emerged as human societies became more established and interconnected during the Upper Paleolithic period. Communities exhibited a division of labor, shared knowledge, and likely developed early language and communication forms. Ritual practices, burial customs, and the creation of personal ornaments reflected a growing sense of identity and cultural significance.
Subsistence Strategies:
The Upper Paleolithic communities in Israel displayed diverse subsistence strategies. Hunting large game, such as deer and ibex, was a crucial aspect of their survival, as evidenced by the remains found at archaeological sites. These communities also practiced gathering wild plants, nuts, and fruits, and may have engaged in fishing and shellfish collection along the Mediterranean coast.
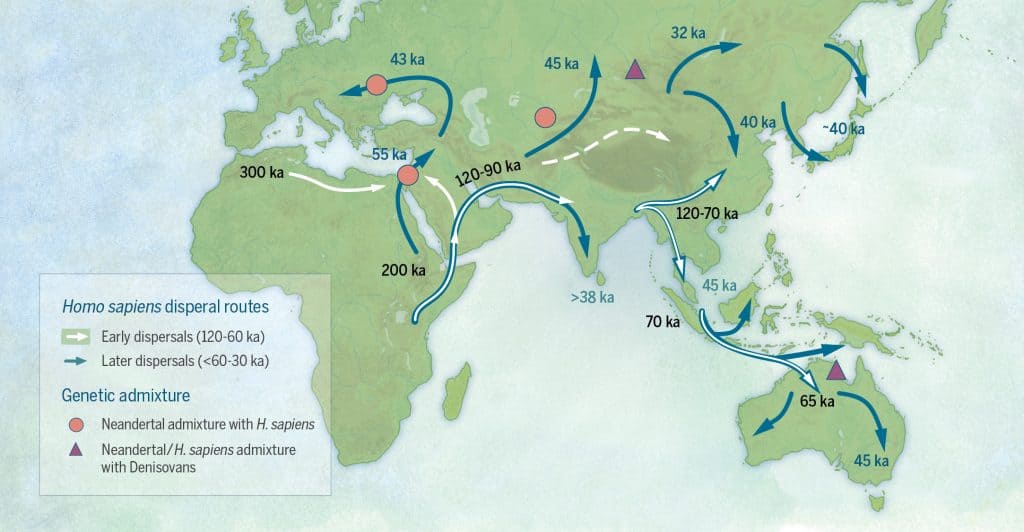
Credit: Katerina Douka & Michelle O’Reilly, Michael D. Petraglia, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Fire and Technology:
Mastering fire was a transformative achievement during the Upper Paleolithic period. Fire provided warmth, protection, and a means to modify the environment. It enabled our ancestors to cook food, extend their activities into the night, and potentially even contribute to developing early communal living forms.
Israel Museum Tour
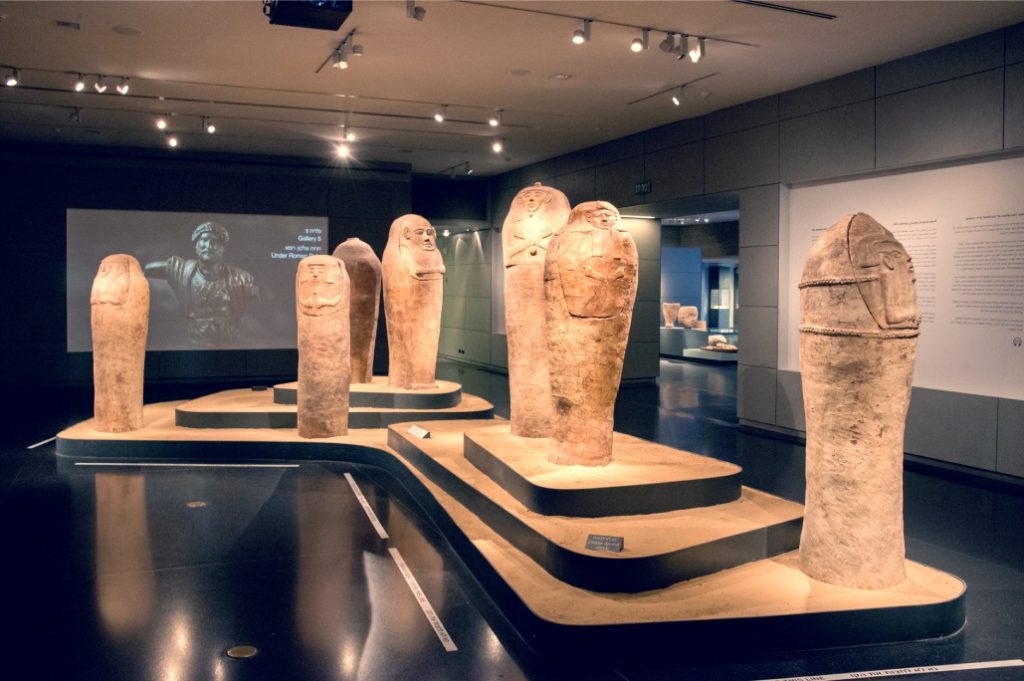

Subsistence Strategies:
Upper Paleolithic communities displayed diverse subsistence strategies, adapting to the available resources in their environments. Hunting large game, such as mammoths, reindeer, and bison, played a crucial role, but gathering plant foods and engaging in fishing and shellfish collection were also essential for sustenance. These strategies demonstrate the resourcefulness and adaptability of our ancient ancestors.
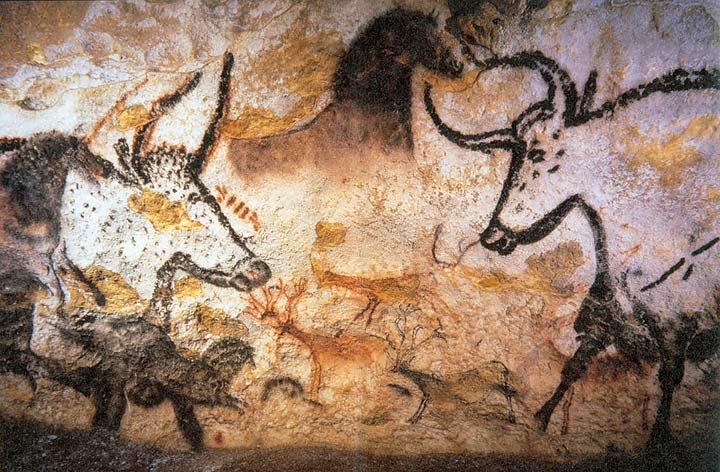

Cultural Complexity and Connections:
The Upper Paleolithic period in Israel reveals evidence of intricate social structures and cultural complexities. Burial sites, personal ornaments, and ritual objects unearthed at sites like Karmel and Hayonim caves suggest the presence of symbolic and spiritual practices. Additionally, the region’s strategic location fostered interactions and cultural exchanges with neighboring communities, influencing the development of regional cultural traits.
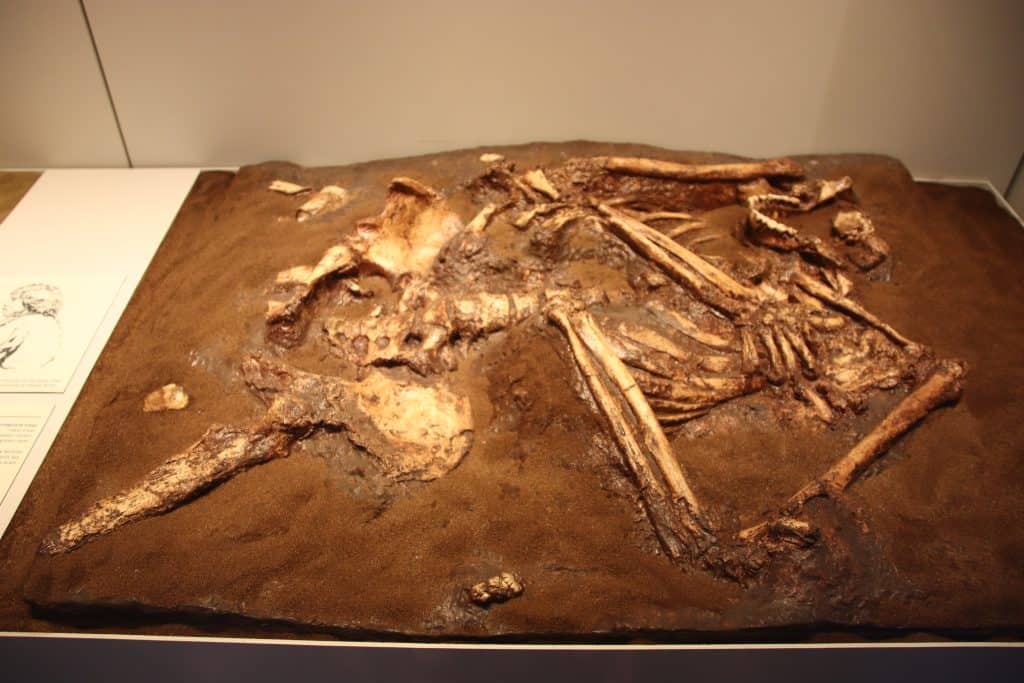

The Legacy of the Upper Paleolithic Period
During the Upper Paleolithic period, she laid the foundation for human ingenuity, cultural diversity, and technological innovation. The art, tools, and social complexity of this era provided the building blocks for future civilizations, shaping the trajectory of our species and influencing the development of subsequent cultures and societies.
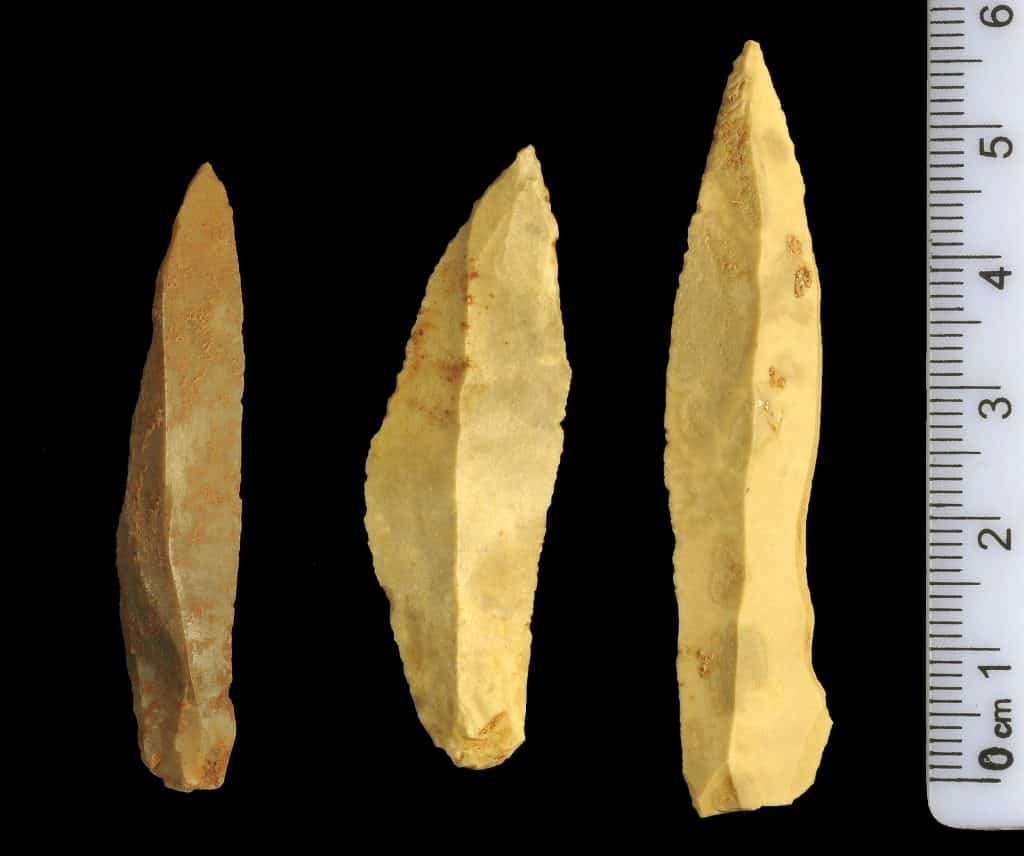

Credit: Manot Cave Expedition, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Unlocking Our Ancient Past:
By studying archaeological sites and meticulously analyzing artifacts, we continue to uncover the secrets of the Upper Paleolithic period. Each discovery adds another piece to the puzzle, allowing us to understand better the rich tapestry of our ancient past and the incredible journey that led us to the present day.

Credit: Avi1111 Dr. Avishai Teicher, Cc By-sa 4.0, Via Wikimedia Commons.
Archaeological Sites in Israel Relatred to the Upper Paleolithic
The country boasts many archaeological sites that provide invaluable insights into the Upper Paleolithic period. Kebara Cave, located in the Carmel Mountains, and Qafzeh and Skhul Caves near the Sea of Galilee are notable sites that have yielded significant discoveries. These sites reveal evidence of human habitation and cultural activities, shedding light on the lives and accomplishments of our ancient ancestors.
Celebrating Human Creativity: As we marvel at our Upper Paleolithic ancestors’ artistic brilliance and technological achievements, let us celebrate the enduring spirit of human creativity and innovation. Their legacy inspires us to embrace our creative potential, fostering a deeper appreciation for human history’s incredible breadth and depth.