The Arab Revolt in Palestine of 1936-1939 was a significant uprising against British rule and Jewish immigration. It was led by Palestinian Arabs and supported by Arab countries and nationalist groups.

1936-1939 Arab Revolt Some Background:
The roots of the 1936-1939 Arab Revolt can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries when Jewish immigration to Palestine increased dramatically. This was driven by the Zionist movement, which sought to establish a Jewish homeland in the region. As Jewish immigration increased, tensions between Jews and Arabs in Palestine grew. In 1917, the British government issued the Balfour Declaration, which declared its support for establishing a Jewish homeland in Palestine. This further exacerbated tensions between Jews and Arabs in the region.

In 1922, the League of Nations granted Britain a mandate over Palestine, which gave Britain control over the territory until it could be granted independence. During the mandate period, Britain supported Jewish immigration and settlement in Palestine, despite strong opposition from Palestinian Arabs.
The Arab Revolt:
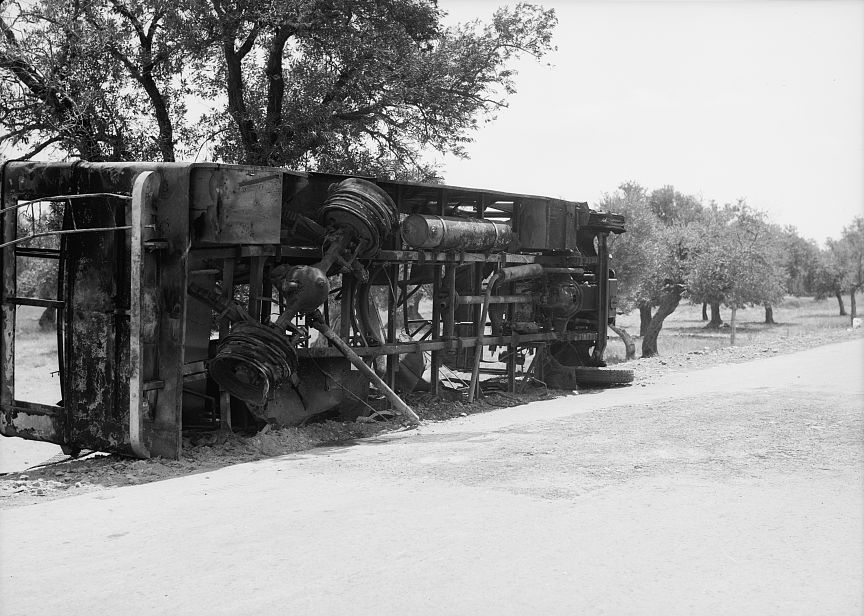
The Arab Revolt began in April 1936, when Palestinian Arab leaders called a general strike to protest British policies and Jewish immigration. The strike quickly turned violent, with Arab militants attacking Jewish communities and British military and civilian targets. The British responded violently, imposing martial law and conducting widespread arrests and detentions. However, the revolt continued to gain momentum, with Arab nationalist groups joining the fight against British rule and Jewish immigration.
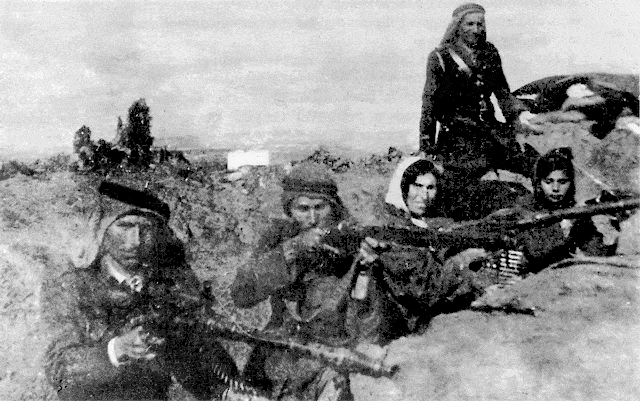
Credit: hanini, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
In 1937, a British-appointed commission led by Lord Peel recommended the partition of Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states. However, this proposal was rejected by both Jews and Arabs, and the violence continued. In 1939, the British government issued the White Paper, which limited Jewish immigration to Palestine and promised to establish a Palestinian state within ten years. This marked the end of the Arab Revolt, as many Palestinian Arab leaders saw the White Paper as a victory for their cause.
Legacy:
The Arab Revolt of 1936-1939 was a significant event in the history of Palestine and the Middle East. It demonstrated the strength of Palestinian nationalism and resistance to British and Jewish rule in the region. It also contributed to the rise of Arab nationalism across the Middle East, as many Arab countries and nationalist groups saw the Palestinian struggle as a symbol of their fight against colonialism and imperialism.

In Conclusion: the legacy of the Arab Revolt continues to be felt today, as the conflict between Israel and Palestine remains one of the world’s most intractable and volatile issues. The root causes of the Arab Revolt – the question of Palestinian statehood, Jewish immigration to Palestine, and the role of colonial powers in the region – continue to shape the ongoing conflict between Israelis and Palestinians.